aiida.orm.nodes.data package¶
Module with Node sub classes for data structures.
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.Data(backend=None, user=None, computer=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.node.NodeThis class is base class for all data objects.
Specifications of the Data class: AiiDA Data objects are subclasses of Node and should have
Multiple inheritance must be supported, i.e. Data should have methods for querying and be able to inherit other library objects such as ASE for structures.
Architecture note: The code plugin is responsible for converting a raw data object produced by code to AiiDA standard object format. The data object then validates itself according to its method. This is done independently in order to allow cross-validation of plugins.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__deepcopy__(memo)[source]¶ Create a clone of the Data node by pipiong through to the clone method and return the result.
Returns: an unstored clone of this Data node
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.data'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_export_format_replacements= {}¶
-
_exportcontent(fileformat, main_file_name='', **kwargs)[source]¶ Converts a Data node to one (or multiple) files.
Note: Export plugins should return utf8-encoded bytes, which can be directly dumped to file.
Parameters: - fileformat (str) – the extension, uniquely specifying the file format.
- main_file_name (str) – (empty by default) Can be used by plugin to infer sensible names for additional files, if necessary. E.g. if the main file is ‘../myplot.gnu’, the plugin may decide to store the dat file under ‘../myplot_data.dat’.
- kwargs – other parameters are passed down to the plugin
Returns: a tuple of length 2. The first element is the content of the otuput file. The second is a dictionary (possibly empty) in the format {filename: filecontent} for any additional file that should be produced.
Return type: (bytes, dict)
-
_get_converters()[source]¶ Get all implemented converter formats. The convention is to find all _get_object_… methods. Returns a list of strings.
-
_get_exporters()[source]¶ Get all implemented export formats. The convention is to find all _prepare_… methods. Returns a dictionary of method_name: method_function
-
_get_importers()[source]¶ Get all implemented import formats. The convention is to find all _parse_… methods. Returns a list of strings.
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.data.Data.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.data.'¶
-
_source_attributes= ['db_name', 'db_uri', 'uri', 'id', 'version', 'extras', 'source_md5', 'description', 'license']¶
-
_storable= True¶
-
_unstorable_message= 'storing for this node has been disabled'¶
-
_validate()[source]¶ Perform validation of the Data object.
Note
validation of data source checks license and requires attribution to be provided in field ‘description’ of source in the case of any CC-BY* license. If such requirement is too strict, one can remove/comment it out.
-
convert(object_format=None, *args)[source]¶ Convert the AiiDA StructureData into another python object
Parameters: object_format – Specify the output format
-
creator¶ Return the creator of this node or None if it does not exist.
Returns: the creating node or None
-
export(path, fileformat=None, overwrite=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Save a Data object to a file.
Parameters: - fname – string with file name. Can be an absolute or relative path.
- fileformat – kind of format to use for the export. If not present, it will try to use the extension of the file name.
- overwrite – if set to True, overwrites file found at path. Default=False
- kwargs – additional parameters to be passed to the _exportcontent method
Returns: the list of files created
-
classmethod
get_export_formats()[source]¶ Get the list of valid export format strings
Returns: a list of valid formats
-
importfile(fname, fileformat=None)[source]¶ Populate a Data object from a file.
Parameters: - fname – string with file name. Can be an absolute or relative path.
- fileformat – kind of format to use for the export. If not present, it will try to use the extension of the file name.
-
importstring(inputstring, fileformat, **kwargs)[source]¶ Converts a Data object to other text format.
Parameters: fileformat – a string (the extension) to describe the file format. Returns: a string with the structure description.
-
source¶ Gets the dictionary describing the source of Data object. Possible fields:
- db_name: name of the source database.
- db_uri: URI of the source database.
- uri: URI of the object’s source. Should be a permanent link.
- id: object’s source identifier in the source database.
- version: version of the object’s source.
- extras: a dictionary with other fields for source description.
- source_md5: MD5 checksum of object’s source.
- description: human-readable free form description of the object’s source.
- license: a string with a type of license.
Note
some limitations for setting the data source exist, see
_validatemethod.Returns: dictionary describing the source of Data object.
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.BaseType(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.DataData sub class to be used as a base for data containers that represent base python data types.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.base'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.base.BaseType.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.base.'¶
-
value¶
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.ArrayData(backend=None, user=None, computer=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.DataStore a set of arrays on disk (rather than on the database) in an efficient way using numpy.save() (therefore, this class requires numpy to be installed).
Each array is stored within the Node folder as a different .npy file.
Note: Before storing, no caching is done: if you perform a get_array()call, the array will be re-read from disk. If instead the ArrayData node has already been stored, the array is cached in memory after the first read, and the cached array is used thereafter. If too much RAM memory is used, you can clear the cache with theclear_internal_cache()method.-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.array.array'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_arraynames_from_files()[source]¶ Return a list of all arrays stored in the node, listing the files (and not relying on the properties).
-
_arraynames_from_properties()[source]¶ Return a list of all arrays stored in the node, listing the attributes starting with the correct prefix.
-
_cached_arrays= None¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.array.array.ArrayData.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.array.array.'¶
-
_validate()[source]¶ Check if the list of .npy files stored inside the node and the list of properties match. Just a name check, no check on the size since this would require to reload all arrays and this may take time and memory.
-
array_prefix= 'array|'¶
-
clear_internal_cache()[source]¶ Clear the internal memory cache where the arrays are stored after being read from disk (used in order to reduce at minimum the readings from disk). This function is useful if you want to keep the node in memory, but you do not want to waste memory to cache the arrays in RAM.
-
delete_array(name)[source]¶ Delete an array from the node. Can only be called before storing.
Parameters: name – The name of the array to delete from the node.
-
get_array(name)[source]¶ Return an array stored in the node
Parameters: name – The name of the array to return.
-
get_arraynames()[source]¶ Return a list of all arrays stored in the node, listing the files (and not relying on the properties).
New in version 0.7: Renamed from arraynames
-
get_iterarrays()[source]¶ Iterator that returns tuples (name, array) for each array stored in the node.
New in version 1.0: Renamed from iterarrays
-
get_shape(name)[source]¶ Return the shape of an array (read from the value cached in the properties for efficiency reasons).
Parameters: name – The name of the array.
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.BandsData(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.array.kpoints.KpointsDataClass to handle bands data
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.array.bands'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_custom_export_format_replacements= {'dat': 'dat_multicolumn', 'gnu': 'gnuplot', 'pdf': 'mpl_pdf', 'png': 'mpl_png', 'py': 'mpl_singlefile'}¶
-
_get_bandplot_data(cartesian, prettify_format=None, join_symbol=None, get_segments=False, y_origin=0.0)[source]¶ Get data to plot a band structure
Parameters: - cartesian – if True, distances (for the x-axis) are computed in cartesian coordinates, otherwise they are computed in reciprocal coordinates. cartesian=True will fail if no cell has been set.
- prettify_format – by default, strings are not prettified. If you want to prettify them, pass a valid prettify_format string (see valid options in the docstring of :py:func:prettify_labels).
- join_symbols – by default, strings are not joined. If you pass a string,
this is used to join strings that are much closer than a given threshold.
The most typical string is the pipe symbol:
|. - get_segments – if True, also computes the band split into segments
- y_origin – if present, shift bands so to set the value specified at
y=0
Returns: a plot_info dictiorary, whose keys are
x(array of distances for the x axis of the plot);y(array of bands),labels(list of tuples in the format (float x value of the label, label string),band_type_idx(array containing an index for each band: if there is only one spin, then it’s an array of zeros, of length equal to the number of bands at each point; if there are two spins, then it’s an array of zeros or ones depending on the type of spin; the length is always equalt to the total number of bands per kpoint).
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_matplotlib_get_dict(main_file_name='', comments=True, title='', legend=None, legend2=None, y_max_lim=None, y_min_lim=None, y_origin=0.0, prettify_format=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Prepare the data to send to the python-matplotlib plotting script.
Parameters: - comments – if True, print comments (if it makes sense for the given format)
- plot_info – a dictionary
- setnumber_offset – an offset to be applied to all set numbers (i.e. s0 is replaced by s[offset], s1 by s[offset+1], etc.)
- color_number – the color number for lines, symbols, error bars and filling (should be less than the parameter max_num_agr_colors defined below)
- title – the title
- legend – the legend (applied only to the first of the set)
- legend2 – the legend for second-type spins (applied only to the first of the set)
- y_max_lim – the maximum on the y axis (if None, put the maximum of the bands)
- y_min_lim – the minimum on the y axis (if None, put the minimum of the bands)
- y_origin – the new origin of the y axis -> all bands are replaced by bands-y_origin
- prettify_format – if None, use the default prettify format. Otherwise specify a string with the prettifier to use.
- kwargs – additional customization variables; only a subset is accepted, see internal variable ‘valid_additional_keywords
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.array.bands.BandsData.'¶
-
_prepare_agr(main_file_name='', comments=True, setnumber_offset=0, color_number=1, color_number2=2, legend='', title='', y_max_lim=None, y_min_lim=None, y_origin=0.0, prettify_format=None)[source]¶ Prepare an xmgrace agr file.
Parameters: - comments – if True, print comments (if it makes sense for the given format)
- plot_info – a dictionary
- setnumber_offset – an offset to be applied to all set numbers (i.e. s0 is replaced by s[offset], s1 by s[offset+1], etc.)
- color_number – the color number for lines, symbols, error bars and filling (should be less than the parameter max_num_agr_colors defined below)
- color_number2 – the color number for lines, symbols, error bars and filling for the second-type spins (should be less than the parameter max_num_agr_colors defined below)
- legend – the legend (applied only to the first set)
- title – the title
- y_max_lim – the maximum on the y axis (if None, put the
maximum of the bands); applied after shifting the origin
by
y_origin - y_min_lim – the minimum on the y axis (if None, put the
minimum of the bands); applied after shifting the origin
by
y_origin - y_origin – the new origin of the y axis -> all bands are replaced by bands-y_origin
- prettify_format – if None, use the default prettify format. Otherwise specify a string with the prettifier to use.
-
_prepare_agr_batch(main_file_name='', comments=True, prettify_format=None)[source]¶ Prepare two files, data and batch, to be plot with xmgrace as: xmgrace -batch file.dat
Parameters: - main_file_name – if the user asks to write the main content on a file, this contains the filename. This should be used to infer a good filename for the additional files. In this case, we remove the extension, and add ‘_data.dat’
- comments – if True, print comments (if it makes sense for the given format)
- prettify_format – if None, use the default prettify format. Otherwise specify a string with the prettifier to use.
-
_prepare_dat_1(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Output data in .dat format, using multiple columns for all y values associated to the same x.
Deprecated since version 0.8.1: Use ‘dat_multicolumn’ format instead
-
_prepare_dat_2(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Output data in .dat format, using blocks.
Deprecated since version 0.8.1: Use ‘dat_block’ format instead
-
_prepare_dat_blocks(main_file_name='', comments=True)[source]¶ Format suitable for gnuplot using blocks. Columns with x and y (path and band energy). Several blocks, separated by two empty lines, one per energy band.
Parameters: comments – if True, print comments (if it makes sense for the given format)
-
_prepare_dat_multicolumn(main_file_name='', comments=True)[source]¶ Write an N x M matrix. First column is the distance between kpoints, The other columns are the bands. Header contains number of kpoints and the number of bands (commented).
Parameters: comments – if True, print comments (if it makes sense for the given format)
-
_prepare_gnuplot(main_file_name='', title='', comments=True, prettify_format=None, y_max_lim=None, y_min_lim=None, y_origin=0.0)[source]¶ Prepare an gnuplot script to plot the bands, with the .dat file returned as an independent file.
Parameters: - main_file_name – if the user asks to write the main content on a file, this contains the filename. This should be used to infer a good filename for the additional files. In this case, we remove the extension, and add ‘_data.dat’
- title – if specified, add a title to the plot
- comments – if True, print comments (if it makes sense for the given format)
- prettify_format – if None, use the default prettify format. Otherwise specify a string with the prettifier to use.
-
_prepare_json(main_file_name='', comments=True)[source]¶ Prepare a json file in a format compatible with the AiiDA band visualizer
Parameters: comments – if True, print comments (if it makes sense for the given format)
-
_prepare_mpl_pdf(main_file_name='', *args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Prepare a python script using matplotlib to plot the bands, with the JSON returned as an independent file.
For the possible parameters, see documentation of
_matplotlib_get_dict()
-
_prepare_mpl_png(main_file_name='', *args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Prepare a python script using matplotlib to plot the bands, with the JSON returned as an independent file.
For the possible parameters, see documentation of
_matplotlib_get_dict()
-
_prepare_mpl_singlefile(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Prepare a python script using matplotlib to plot the bands
For the possible parameters, see documentation of
_matplotlib_get_dict()
-
_prepare_mpl_withjson(main_file_name='', *args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Prepare a python script using matplotlib to plot the bands, with the JSON returned as an independent file.
For the possible parameters, see documentation of
_matplotlib_get_dict()
-
_query_type_string= 'data.array.bands.'¶
-
_validate_bands_occupations(bands, occupations=None, labels=None)[source]¶ Validate the list of bands and of occupations before storage. Kpoints must be set in advance. Bands and occupations must be convertible into arrays of Nkpoints x Nbands floats or Nspins x Nkpoints x Nbands; Nkpoints must correspond to the number of kpoints.
-
array_labels¶ Get the labels associated with the band arrays
-
get_bands(also_occupations=False, also_labels=False)[source]¶ Returns an array (nkpoints x num_bands or nspins x nkpoints x num_bands) of energies. :param also_occupations: if True, returns also the occupations array. Default = False
-
set_bands(bands, units=None, occupations=None, labels=None)[source]¶ Set an array of band energies of dimension (nkpoints x nbands). Kpoints must be set in advance. Can contain floats or None. :param bands: a list of nkpoints lists of nbands bands, or a 2D array of shape (nkpoints x nbands), with band energies for each kpoint :param units: optional, energy units :param occupations: optional, a 2D list or array of floats of same shape as bands, with the occupation associated to each band
-
set_kpointsdata(kpointsdata)[source]¶ Load the kpoints from a kpoint object. :param kpointsdata: an instance of KpointsData class
-
show_mpl(**kwargs)[source]¶ Call a show() command for the band structure using matplotlib. This uses internally the ‘mpl_singlefile’ format, with empty main_file_name.
Other kwargs are passed to self._exportcontent.
-
units¶ Units in which the data in bands were stored. A string
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.KpointsData(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.array.array.ArrayDataClass to handle array of kpoints in the Brillouin zone. Provide methods to generate either user-defined k-points or path of k-points along symmetry lines. Internally, all k-points are defined in terms of crystal (fractional) coordinates. Cell and lattice vector coordinates are in Angstroms, reciprocal lattice vectors in Angstrom^-1 . :note: The methods setting and using the Bravais lattice info assume the PRIMITIVE unit cell is provided in input to the set_cell or set_cell_from_structure methods.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.array.kpoints'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_change_reference(kpoints, to_cartesian=True)[source]¶ Change reference system, from cartesian to crystal coordinates (units of b1,b2,b3) or viceversa. :param kpoints: a list of (3) point coordinates :return kpoints: a list of (3) point coordinates in the new reference
-
_dimension¶ Dimensionality of the structure, found from its pbc (i.e. 1 if it’s a 1D structure, 2 if its 2D, 3 if it’s 3D …). :return dimensionality: 0, 1, 2 or 3 :note: will return 3 if pbc has not been set beforehand
-
_find_bravais_info(epsilon_length=1e-05, epsilon_angle=1e-05)[source]¶ Finds the Bravais lattice of the cell passed in input to the Kpoint class :note: We assume that the cell given by the cell property is the primitive unit cell.
Deprecated since version 0.11: Use the methods inside the aiida.tools.data.array.kpoints module instead.
Returns: a dictionary, with keys short_name, extended_name, index (index of the Bravais lattice), and sometimes variation (name of the variation of the Bravais lattice) and extra (a dictionary with extra parameters used by the get_special_points method)
-
_get_or_create_bravais_lattice(epsilon_length=1e-05, epsilon_angle=1e-05)[source]¶ Try to get the bravais_lattice info if stored already, otherwise analyze the cell with the default settings and save this in the attribute.
Deprecated since version 0.11: Use the methods inside the aiida.tools.data.array.kpoints module instead.
Parameters: - epsilon_length – threshold on lengths comparison, used to get the bravais lattice info
- epsilon_angle – threshold on angles comparison, used to get the bravais lattice info
Return bravais_lattice: the dictionary containing the symmetry info
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.array.kpoints.KpointsData.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.array.kpoints.'¶
-
_set_bravais_lattice(value)[source]¶ Validating function to set the bravais_lattice dictionary
Deprecated since version 0.11.
-
_set_cell(value)[source]¶ Validate if ‘value’ is a allowed crystal unit cell :param value: something compatible with a 3x3 tuple of floats
-
_set_labels(value)[source]¶ set label names. Must pass in input a list like:
[[0,'X'],[34,'L'],... ]
-
_set_reciprocal_cell()[source]¶ Sets the reciprocal cell in units of 1/Angstrom from the internally set cell
-
_validate_kpoints_weights(kpoints, weights)[source]¶ Validate the list of kpoints and of weights before storage. Kpoints and weights must be convertible respectively to an array of N x dimension and N floats
-
bravais_lattice¶ The dictionary containing informations about the cell symmetry
Deprecated since version 0.11.
-
cell¶ The crystal unit cell. Rows are the crystal vectors in Angstroms. :return: a 3x3 numpy.array
-
find_bravais_lattice(epsilon_length=1e-05, epsilon_angle=1e-05)[source]¶ Analyze the symmetry of the cell. Allows to relax or tighten the thresholds used to compare angles and lengths of the cell. Save the information of the cell used for later use (like getting special points). It has to be used if the user wants to be sure the right symmetries are recognized. Otherwise, this function is automatically called with the default values.
If the right symmetry is not found, be sure also you are providing cells with enough digits.
If node is already stored, just returns the symmetry found before storing (if any).
Deprecated since version 0.11: Use the methods inside the aiida.tools.data.array.kpoints module instead.
Return (str) lattice_name: the name of the bravais lattice and its eventual variation
-
get_description()[source]¶ Returns a string with infos retrieved from kpoints node’s properties. :param node: :return: retstr
-
get_kpoints(also_weights=False, cartesian=False)[source]¶ Return the list of kpoints
Parameters: - also_weights – if True, returns also the list of weights. Default = False
- cartesian – if True, returns points in cartesian coordinates, otherwise, returns in crystal coordinates. Default = False.
-
get_kpoints_mesh(print_list=False)[source]¶ Get the mesh of kpoints.
Parameters: print_list – default=False. If True, prints the mesh of kpoints as a list Raises: AttributeError – if no mesh has been set Return mesh,offset: (if print_list=False) a list of 3 integers and a list of three floats 0<x<1, representing the mesh and the offset of kpoints Return kpoints: (if print_list = True) an explicit list of kpoints coordinates, similar to what returned by get_kpoints()
-
get_special_points(cartesian=False, epsilon_length=1e-05, epsilon_angle=1e-05)[source]¶ Get the special point and path of a given structure.
References:
- In 2D, coordinates are based on the paper: R. Ramirez and M. C. Bohm, Int. J. Quant. Chem., XXX, pp. 391-411 (1986)
- In 3D, coordinates are based on the paper: W. Setyawan, S. Curtarolo, Comp. Mat. Sci. 49, 299 (2010)
Deprecated since version 0.11: Use the methods inside the aiida.tools.data.array.kpoints module instead.
Parameters: - cartesian – If true, returns points in cartesian coordinates. Crystal coordinates otherwise. Default=False
- epsilon_length – threshold on lengths comparison, used to get the bravais lattice info
- epsilon_angle – threshold on angles comparison, used to get the bravais lattice info
Returns point_coords: a dictionary of point_name:point_coords key,values.
Returns path: the suggested path which goes through all high symmetry lines. A list of lists for all path segments. e.g. [(‘G’,’X’),(‘X’,’M’),…] It’s not necessarily a continuous line.
Note: We assume that the cell given by the cell property is the primitive unit cell
-
labels¶ Labels associated with the list of kpoints. List of tuples with kpoint index and kpoint name:
[(0,'G'),(13,'M'),...]
-
pbc¶ The periodic boundary conditions along the vectors a1,a2,a3.
Returns: a tuple of three booleans, each one tells if there are periodic boundary conditions for the i-th real-space direction (i=1,2,3)
-
set_cell(cell, pbc=None)[source]¶ Set a cell to be used for symmetry analysis. To set a cell from an AiiDA structure, use “set_cell_from_structure”.
Parameters: - cell – 3x3 matrix of cell vectors. Orientation: each row represent a lattice vector. Units are Angstroms.
- pbc – list of 3 booleans, True if in the nth crystal direction the structure is periodic. Default = [True,True,True]
-
set_cell_from_structure(structuredata)[source]¶ Set a cell to be used for symmetry analysis from an AiiDA structure. Inherits both the cell and the pbc’s. To set manually a cell, use “set_cell”
Parameters: structuredata – an instance of StructureData
-
set_kpoints(kpoints, cartesian=False, labels=None, weights=None, fill_values=0)[source]¶ Set the list of kpoints. If a mesh has already been stored, raise a ModificationNotAllowed
Parameters: - kpoints –
a list of kpoints, each kpoint being a list of one, two or three coordinates, depending on self.pbc: if structure is 1D (only one True in self.pbc) one allows singletons or scalars for each k-point, if it’s 2D it can be a length-2 list, and in all cases it can be a length-3 list. Examples:
- [[0.,0.,0.],[0.1,0.1,0.1],…] for 1D, 2D or 3D
- [[0.,0.],[0.1,0.1,],…] for 1D or 2D
- [[0.],[0.1],…] for 1D
- [0., 0.1, …] for 1D (list of scalars)
For 0D (all pbc are False), the list can be any of the above or empty - then only Gamma point is set. The value of k for the non-periodic dimension(s) is set by fill_values
- cartesian – if True, the coordinates given in input are treated as in cartesian units. If False, the coordinates are crystal, i.e. in units of b1,b2,b3. Default = False
- labels – optional, the list of labels to be set for some of the kpoints. See labels for more info
- weights – optional, a list of floats with the weight associated to the kpoint list
- fill_values – scalar to be set to all non-periodic dimensions (indicated by False in self.pbc), or list of values for each of the non-periodic dimensions.
- kpoints –
-
set_kpoints_mesh(mesh, offset=[0.0, 0.0, 0.0])[source]¶ Set KpointsData to represent a uniformily spaced mesh of kpoints in the Brillouin zone. This excludes the possibility of set/get kpoints
Parameters: - mesh – a list of three integers, representing the size of the kpoint mesh along b1,b2,b3.
- offset – (optional) a list of three floats between 0 and 1. [0.,0.,0.] is Gamma centered mesh [0.5,0.5,0.5] is half shifted [1.,1.,1.] by periodicity should be equivalent to [0.,0.,0.] Default = [0.,0.,0.].
-
set_kpoints_mesh_from_density(distance, offset=[0.0, 0.0, 0.0], force_parity=False)[source]¶ Set a kpoints mesh using a kpoints density, expressed as the maximum distance between adjacent points along a reciprocal axis
Parameters: - distance – distance (in 1/Angstrom) between adjacent
kpoints, i.e. the number of kpoints along each reciprocal
axis i is
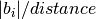 where
where 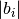 is the norm of the reciprocal cell vector.
is the norm of the reciprocal cell vector. - offset – (optional) a list of three floats between 0 and 1. [0.,0.,0.] is Gamma centered mesh [0.5,0.5,0.5] is half shifted Default = [0.,0.,0.].
- force_parity – (optional) if True, force each integer in the mesh to be even (except for the non-periodic directions).
Note: a cell should be defined first.
Note: the number of kpoints along non-periodic axes is always 1.
- distance – distance (in 1/Angstrom) between adjacent
kpoints, i.e. the number of kpoints along each reciprocal
axis i is
-
set_kpoints_path(value=None, kpoint_distance=None, cartesian=False, epsilon_length=1e-05, epsilon_angle=1e-05)[source]¶ Set a path of kpoints in the Brillouin zone.
Deprecated since version 0.11: Use the methods inside the aiida.tools.data.array.kpoints module instead.
Parameters: - value –
description of the path, in various possible formats.
None: automatically sets all irreducible high symmetry paths. Requires that a cell was set
or
[(‘G’,’M’), (…), …] [(‘G’,’M’,30), (…), …] [(‘G’,(0,0,0),’M’,(1,1,1)), (…), …] [(‘G’,(0,0,0),’M’,(1,1,1),30), (…), …]
- cartesian (bool) – if set to true, reads the coordinates eventually passed in value as cartesian coordinates. Default: False.
- kpoint_distance (float) – parameter controlling the distance between kpoints. Distance is given in crystal coordinates, i.e. the distance is computed in the space of b1,b2,b3. The distance set will be the closest possible to this value, compatible with the requirement of putting equispaced points between two special points (since extrema are included).
- epsilon_length (float) – threshold on lengths comparison, used to get the bravais lattice info. It has to be used if the user wants to be sure the right symmetries are recognized.
- epsilon_angle (float) – threshold on angles comparison, used to get the bravais lattice info. It has to be used if the user wants to be sure the right symmetries are recognized.
- value –
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.ProjectionData(backend=None, user=None, computer=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.orbital.OrbitalData,aiida.orm.nodes.data.array.array.ArrayDataA class to handle arrays of projected wavefunction data. That is projections of a orbitals, usually an atomic-hydrogen orbital, onto a given bloch wavefunction, the bloch wavefunction being indexed by s, n, and k. E.g. the elements are the projections described as < orbital | Bloch wavefunction (s,n,k) >
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.array.projection'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_check_projections_bands(projection_array)[source]¶ Checks to make sure that a reference bandsdata is already set, and that projection_array is of the same shape of the bands data
Parameters: projwfc_arrays – nk x nb x nwfc array, to be checked against bands Raise: AttributeError if energy is not already set Raise: AttributeError if input_array is not of same shape as dos_energy
-
_find_orbitals_and_indices(**kwargs)[source]¶ Finds all the orbitals and their indicies associated with kwargs essential for retrieving the other indexed array parameters
Parameters: kwargs – kwargs that can call orbitals as in get_orbitals() Returns: retrieve_indexes, list of indicicies of orbitals corresponding to the kwargs Returns: all_orbitals, list of orbitals to which the indexes correspond
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.array.projection.ProjectionData.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.array.projection.'¶
-
get_pdos(**kwargs)[source]¶ Retrieves all the pdos arrays corresponding to the input kwargs
Parameters: kwargs – inputs describing the orbitals associated with the pdos arrays Returns: a list of tuples containing the orbital, energy array and pdos array associated with all orbitals that correspond to kwargs
-
get_projections(**kwargs)[source]¶ Retrieves all the pdos arrays corresponding to the input kwargs
Parameters: kwargs – inputs describing the orbitals associated with the pdos arrays Returns: a list of tuples containing the orbital, and projection arrays associated with all orbitals that correspond to kwargs
-
get_reference_bandsdata()[source]¶ Returns the reference BandsData, using the set uuid via set_reference_bandsdata
Returns: a BandsData instance
Raises: - AttributeError – if the bandsdata has not been set yet
- exceptions.NotExistent – if the bandsdata uuid did not retrieve bandsdata
-
set_orbitals(**kwargs)[source]¶ This method is inherited from OrbitalData, but is blocked here. If used will raise a NotImplementedError
-
set_projectiondata(list_of_orbitals, list_of_projections=None, list_of_energy=None, list_of_pdos=None, tags=None, bands_check=True)[source]¶ Stores the projwfc_array using the projwfc_label, after validating both.
Parameters: - list_of_orbitals – list of orbitals, of class orbital data. They should be the ones up on which the projection array corresponds with.
- list_of_projections – list of arrays of projections of a atomic wavefunctions onto bloch wavefunctions. Since the projection is for every bloch wavefunction which can be specified by its spin (if used), band, and kpoint the dimensions must be nspin x nbands x nkpoints for the projwfc array. Or nbands x nkpoints if spin is not used.
- energy_axis – list of energy axis for the list_of_pdos
- list_of_pdos – a list of projected density of states for the atomic wavefunctions, units in states/eV
- tags – A list of tags, not supported currently.
- bands_check – if false, skips checks of whether the bands has been already set, and whether the sizes match. For use in parsers, where the BandsData has not yet been stored and therefore get_reference_bandsdata cannot be called
-
set_reference_bandsdata(value)[source]¶ Sets a reference bandsdata, creates a uuid link between this data object and a bandsdata object, must be set before any projection arrays
Parameters: value – a BandsData instance, a uuid or a pk Raise: exceptions.NotExistent if there was no BandsData associated with uuid or pk
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.TrajectoryData(structurelist=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.array.array.ArrayDataStores a trajectory (a sequence of crystal structures with timestamps, and possibly with velocities).
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(structurelist=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.array.trajectory'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_get_aiida_structure(store=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Creates
aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure.StructureData.Parameters: - converter – specify the converter. Default ‘ase’.
- store – If True, intermediate calculation gets stored in the AiiDA database for record. Default False.
Returns:
-
_get_cif(index=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Creates
aiida.orm.nodes.data.cif.CifData
-
_internal_validate(stepids, cells, symbols, positions, times, velocities)[source]¶ Internal function to validate the type and shape of the arrays. See the documentation of py:meth:.set_trajectory for a description of the valid shape and type of the parameters.
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_parse_xyz_pos(inputstring)[source]¶ Load positions from a XYZ file.
Note
The steps and symbols must be set manually before calling this import function as a consistency measure. Even though the symbols and steps could be extracted from the XYZ file, the data present in the XYZ file may or may not be correct and the same logic would have to be present in the XYZ-velocities function. It was therefore decided not to implement it at all but require it to be set explicitly.
Usage:
from aiida.orm.nodes.data.array.trajectory import TrajectoryData t = TrajectoryData() # get sites and number of timesteps t.set_array('steps', arange(ntimesteps)) t.set_array('symbols', array([site.kind for site in s.sites])) t.importfile('some-calc/AIIDA-PROJECT-pos-1.xyz', 'xyz_pos')
-
_parse_xyz_vel(inputstring)[source]¶ Load velocities from a XYZ file.
Note
The steps and symbols must be set manually before calling this import function as a consistency measure. See also comment for
_parse_xyz_pos()
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.array.trajectory.TrajectoryData.'¶
-
_prepare_cif(trajectory_index=None, main_file_name='')[source]¶ Write the given trajectory to a string of format CIF.
-
_prepare_tcod(main_file_name='', **kwargs)[source]¶ Write the given trajectory to a string of format TCOD CIF.
-
_prepare_xsf(index=None, main_file_name='')[source]¶ Write the given trajectory to a string of format XSF (for XCrySDen).
-
_query_type_string= 'data.array.trajectory.'¶
-
_validate()[source]¶ Verify that the required arrays are present and that their type and dimension are correct.
-
get_cells()[source]¶ Return the array of cells, if it has already been set.
Raises: KeyError – if the trajectory has not been set yet.
-
get_cif(index=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Creates
aiida.orm.nodes.data.cif.CifDataNew in version 1.0: Renamed from _get_cif
-
get_index_from_stepid(stepid)[source]¶ Given a value for the stepid (i.e., a value among those of the
stepsarray), return the array index of that stepid, that can be used in other methods such asget_step_data()orget_step_structure().New in version 0.7: Renamed from get_step_index
Note
Note that this function returns the first index found (i.e. if multiple steps are present with the same value, only the index of the first one is returned).
Raises: ValueError – if no step with the given value is found.
-
get_positions()[source]¶ Return the array of positions, if it has already been set.
Raises: KeyError – if the trajectory has not been set yet.
-
get_step_data(index)[source]¶ Return a tuple with all information concerning the stepid with given index (0 is the first step, 1 the second step and so on). If you know only the step value, use the
get_index_from_stepid()method to get the corresponding index.If no velocities were specified, None is returned as the last element.
Returns: A tuple in the format
(stepid, time, cell, symbols, positions, velocities), wherestepidis an integer,timeis a float,cellis a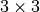 matrix,
matrix, symbolsis an array of lengthn, positions is a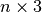 array, and velocities is either
array, and velocities is either
Noneor a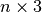 array
arrayParameters: index – The index of the step that you want to retrieve, from 0 to
self.numsteps - 1.Raises: - IndexError – if you require an index beyond the limits.
- KeyError – if you did not store the trajectory yet.
-
get_step_structure(index, custom_kinds=None)[source]¶ Return an AiiDA
aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure.StructureDatanode (not stored yet!) with the coordinates of the given step, identified by its index. If you know only the step value, use theget_index_from_stepid()method to get the corresponding index.Note
The periodic boundary conditions are always set to True.
New in version 0.7: Renamed from step_to_structure
Parameters: - index – The index of the step that you want to retrieve, from
0 to
self.numsteps- 1. - custom_kinds – (Optional) If passed must be a list of
aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure.Kindobjects. There must be one kind object for each different string in thesymbolsarray, withkind.nameset to this string. If this parameter is omitted, the automatic kind generation of AiiDAaiida.orm.nodes.data.structure.StructureDatanodes is used, meaning that the strings in thesymbolsarray must be valid chemical symbols.
- index – The index of the step that you want to retrieve, from
0 to
-
get_stepids()[source]¶ Return the array of steps, if it has already been set.
New in version 0.7: Renamed from get_steps
Raises: KeyError – if the trajectory has not been set yet.
-
get_structure(store=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Creates
aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure.StructureData.New in version 1.0: Renamed from _get_aiida_structure
Parameters: - converter – specify the converter. Default ‘ase’.
- store – If True, intermediate calculation gets stored in the AiiDA database for record. Default False.
Returns:
-
get_times()[source]¶ Return the array of times (in ps), if it has already been set.
Raises: KeyError – if the trajectory has not been set yet.
-
get_velocities()[source]¶ Return the array of velocities, if it has already been set.
Note
This function (differently from all other
get_*functions, will not raise an exception if the velocities are not set, but rather returnNone(both if no trajectory was not set yet, and if it the trajectory was set but no velocities were specified).
-
numsites¶ Return the number of stored sites, or zero if nothing has been stored yet.
-
numsteps¶ Return the number of stored steps, or zero if nothing has been stored yet.
-
set_structurelist(structurelist)[source]¶ Create trajectory from the list of
aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure.StructureDatainstances.Parameters: structurelist – a list of aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure.StructureDatainstances.Raises: ValueError – if symbol lists of supplied structures are different
-
set_trajectory(symbols, positions, stepids=None, cells=None, times=None, velocities=None)[source]¶ Store the whole trajectory, after checking that types and dimensions are correct.
Parameters
stepids,cellsandvelocitiesare optional variables. If nothing is passed forcellsorvelocitiesnothing will be stored. However, if no input is given forstepidsa consecutive sequence [0,1,2,…,len(positions)-1] will be assumed.Parameters: - symbols – string list with dimension
n, wherenis the number of atoms (i.e., sites) in the structure. The same list is used for each step. Normally, the string should be a valid chemical symbol, but actually any unique string works and can be used as the name of the atomic kind (see also theget_step_structure()method). - positions – float array with dimension
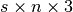 ,
where
,
where sis the length of thestepidsarray andnis the length of thesymbolsarray. Units are angstrom. In particular,positions[i,j,k]is thek-th component of thej-th atom (or site) in the structure at the time step with indexi(identified by step numberstep[i]and with timestamptimes[i]). - stepids – integer array with dimension
s, wheresis the number of steps. Typically represents an internal counter within the code. For instance, if you want to store a trajectory with one step every 10, starting from step 65, the array will be[65,75,85,...]. No checks are done on duplicate elements or on the ordering, but anyway this array should be sorted in ascending order, without duplicate elements. (If not specified, stepids will be set tonumpy.arange(s)by default) It is internally stored as an array named ‘steps’. - cells – if specified float array with dimension
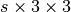 , where
, where sis the length of thestepidsarray. Units are angstrom. In particular,cells[i,j,k]is thek-th component of thej-th cell vector at the time step with indexi(identified by step numberstepid[i]and with timestamptimes[i]). - times – if specified, float array with dimension
s, wheresis the length of thestepidsarray. Contains the timestamp of each step in picoseconds (ps). - velocities – if specified, must be a float array with the same
dimensions of the
positionsarray. The array contains the velocities in the atoms.
Todo
Choose suitable units for velocities
- symbols – string list with dimension
-
show_mpl_pos(**kwargs)[source]¶ Shows the positions as a function of time, separate for XYZ coordinates
Parameters: - stepsize (int) – The stepsize for the trajectory, set higher than 1 to reduce number of points
- mintime (int) – Time to start from
- maxtime (int) – Maximum time
- elements (list) – A list of atomic symbols that should be displayed. If not specified, all atoms are displayed.
- indices (list) – A list of indices of that atoms that can be displayed. If not specified, all atoms of the correct species are displayed.
- dont_block (bool) – If True, interpreter is not blocked when figure is displayed.
-
symbols¶ Return the array of symbols, if it has already been set.
Raises: KeyError – if the trajectory has not been set yet.
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.XyData(backend=None, user=None, computer=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.array.array.ArrayDataA subclass designed to handle arrays that have an “XY” relationship to each other. That is there is one array, the X array, and there are several Y arrays, which can be considered functions of X.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.array.xy'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_arrayandname_validator(array, name, units)[source]¶ Validates that the array is an numpy.ndarray and that the name is of type basestring. Raises InputValidationError if this not the case.
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.array.xy.XyData.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.array.xy.'¶
-
get_x()[source]¶ Tries to retrieve the x array and x name raises a NotExistent exception if no x array has been set yet. :return x_name: the name set for the x_array :return x_array: the x array set earlier :return x_units: the x units set earlier
-
get_y()[source]¶ Tries to retrieve the y arrays and the y names, raises a NotExistent exception if they have not been set yet, or cannot be retrieved :return y_names: list of strings naming the y_arrays :return y_arrays: list of y_arrays :return y_units: list of strings giving the units for the y_arrays
-
set_x(x_array, x_name, x_units)[source]¶ Sets the array and the name for the x values.
Parameters: - x_array – A numpy.ndarray, containing only floats
- x_name – a string for the x array name
- x_units – the units of x
-
set_y(y_arrays, y_names, y_units)[source]¶ Set array(s) for the y part of the dataset. Also checks if the x_array has already been set, and that, the shape of the y_arrays agree with the x_array. :param y_arrays: A list of y_arrays, numpy.ndarray :param y_names: A list of strings giving the names of the y_arrays :param y_units: A list of strings giving the units of the y_arrays
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.Bool(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.base.BaseTypeData sub class to represent a boolean value.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.bool'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.bool.Bool.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.bool.'¶
-
_type¶ alias of
__builtin__.bool
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.CifData(ase=None, filepath=None, values=None, source=None, scan_type='standard', parse_policy='eager', **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.singlefile.SinglefileDataWrapper for Crystallographic Interchange File (CIF)
Note
the filepath (physical) is held as the authoritative source of information, so all conversions are done through the physical file: when setting
aseorvalues, a physical CIF file is generated first, the values are updated from the physical CIF file.-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(ase=None, filepath=None, values=None, source=None, scan_type='standard', parse_policy='eager', **kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.cif'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_ase= None¶
-
_get_aiida_structure(converter='pymatgen', store=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Creates
aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure.StructureData.Parameters: - converter – specify the converter. Default ‘pymatgen’.
- store – if True, intermediate calculation gets stored in the AiiDA database for record. Default False.
- primitive_cell – if True, primitive cell is returned, conventional cell if False. Default False.
- occupancy_tolerance – If total occupancy of a site is between 1 and occupancy_tolerance, the occupancies will be scaled down to 1. (pymatgen only)
- site_tolerance – This tolerance is used to determine if two sites are sitting in the same position, in which case they will be combined to a single disordered site. Defaults to 1e-4. (pymatgen only)
Returns:
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_parse_policies= ('eager', 'lazy')¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.cif.CifData.'¶
-
_prepare_cif(main_file_name='')[source]¶ Return CIF string of CifData object.
If parsed values are present, a CIF string is created and written to file. If no parsed values are present, the CIF string is read from file.
-
_prepare_tcod(main_file_name='', **kwargs)[source]¶ Write the given CIF to a string of format TCOD CIF.
-
_query_type_string= 'data.cif.'¶
-
_scan_types= ('standard', 'flex')¶
-
_set_incompatibilities= [('ase', 'filepath'), ('ase', 'values'), ('filepath', 'values')]¶
-
_values= None¶
-
ase¶ ASE object, representing the CIF.
Note
requires ASE module.
-
classmethod
from_md5(md5)[source]¶ Return a list of all CIF files that match a given MD5 hash.
Note
the hash has to be stored in a
_md5attribute, otherwise the CIF file will not be found.
-
get_ase(**kwargs)[source]¶ Returns ASE object, representing the CIF. This function differs from the property
aseby the possibility to pass the keyworded arguments (kwargs) to ase.io.cif.read_cif().Note
requires ASE module.
-
get_formulae(mode='sum')[source]¶ Return chemical formulae specified in CIF file.
Note: This does not compute the formula, it only reads it from the appropriate tag. Use refine_inline to compute formulae.
-
classmethod
get_or_create(filename, use_first=False, store_cif=True)[source]¶ Pass the same parameter of the init; if a file with the same md5 is found, that CifData is returned.
Parameters: - filename – an absolute filename on disk
- use_first – if False (default), raise an exception if more than one CIF file is found. If it is True, instead, use the first available CIF file.
- store_cif (bool) – If false, the CifData objects are not stored in the database. default=True.
Return (cif, created): where cif is the CifData object, and create is either True if the object was created, or False if the object was retrieved from the DB.
-
get_structure(converter='pymatgen', store=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Creates
aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure.StructureData.New in version 1.0: Renamed from _get_aiida_structure
Parameters: - converter – specify the converter. Default ‘pymatgen’.
- store – if True, intermediate calculation gets stored in the AiiDA database for record. Default False.
- primitive_cell – if True, primitive cell is returned, conventional cell if False. Default False.
- occupancy_tolerance – If total occupancy of a site is between 1 and occupancy_tolerance, the occupancies will be scaled down to 1. (pymatgen only)
- site_tolerance – This tolerance is used to determine if two sites are sitting in the same position, in which case they will be combined to a single disordered site. Defaults to 1e-4. (pymatgen only)
Returns:
-
has_atomic_sites¶ Returns whether there are any atomic sites defined in the cif data. That is to say, it will check all the values for the _atom_site_fract_* tags and if they are all equal to ? that means there are no relevant atomic sites defined and the function will return False. In all other cases the function will return True
Returns: False when at least one atomic site fractional coordinate is not equal to ? and True otherwise
-
has_attached_hydrogens¶ Check if there are hydrogens without coordinates, specified as attached to the atoms of the structure.
Returns: True if there are attached hydrogens, False otherwise.
-
has_partial_occupancies¶ Return if the cif data contains partial occupancies
A partial occupancy is defined as site with an occupancy that differs from unity, within a precision of 1E-6
Returns: True if there are partial occupancies, False otherwise
-
has_undefined_atomic_sites¶ Return whether the cif data contains any undefined atomic sites.
An undefined atomic site is defined as a site where at least one of the fractional coordinates specified in the _atom_site_fract_* tags, cannot be successfully interpreted as a float. If the cif data contains any site that matches this description, or it does not contain any atomic site tags at all, the cif data is said to have undefined atomic sites.
Returns: boolean, True if no atomic sites are defined or if any of the defined sites contain undefined positions and False otherwise
-
has_unknown_species¶ Returns whether the cif contains atomic species that are not recognized by AiiDA.
The known species are taken from the elements dictionary in aiida.common.constants, with the exception of the “unknown” placeholder element with symbol ‘X’, as this could not be used to construct a real structure. If any of the formula of the cif data contain species that are not in that elements dictionary, the function will return True and False in all other cases. If there is no formulae to be found, it will return None
Returns: True when there are unknown species in any of the formulae, False if not, None if no formula found
-
parse(scan_type=None)[source]¶ Parses CIF file and sets attributes.
Parameters: scan_type – See set_scan_type
-
put_object_from_file(path, key=None, mode='w', encoding='utf8', force=False)[source]¶ Set the file.
If the source is set and the MD5 checksum of new file is different from the source, the source has to be deleted.
-
static
read_cif(fileobj, index=-1, **kwargs)[source]¶ A wrapper method that simulates the behavior of the old function ase.io.cif.read_cif by using the new generic ase.io.read function.
-
set_ase(aseatoms)[source]¶ Set the contents of the CifData starting from an ASE atoms object
Parameters: aseatoms – the ASE atoms object
-
set_parse_policy(parse_policy)[source]¶ Set the parse policy.
Parameters: parse_policy – Either ‘eager’ (parse CIF file on set_file) or ‘lazy’ (defer parsing until needed)
-
set_scan_type(scan_type)[source]¶ Set the scan_type for PyCifRW.
The ‘flex’ scan_type of PyCifRW is faster for large CIF files but does not yet support the CIF2 format as of 02/2018. See the CifFile.ReadCif function
Parameters: scan_type – Either ‘standard’ or ‘flex’ (see _scan_types)
-
set_values(values)[source]¶ Set internal representation to values.
Warning: This also writes a new CIF file.
Parameters: values – PyCifRW CifFile object Note
requires PyCifRW module.
-
values¶ PyCifRW structure, representing the CIF datablocks.
Note
requires PyCifRW module.
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.Code(remote_computer_exec=None, local_executable=None, input_plugin_name=None, files=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.DataA code entity. It can either be ‘local’, or ‘remote’.
- Local code: it is a collection of files/dirs (added using the add_path() method), where one file is flagged as executable (using the set_local_executable() method).
- Remote code: it is a pair (remotecomputer, remotepath_of_executable) set using the set_remote_computer_exec() method.
For both codes, one can set some code to be executed right before or right after the execution of the code, using the set_preexec_code() and set_postexec_code() methods (e.g., the set_preexec_code() can be used to load specific modules required for the code to be run).
-
HIDDEN_KEY= 'hidden'¶
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(remote_computer_exec=None, local_executable=None, input_plugin_name=None, files=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.code'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.code.Code.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.code.'¶
-
_set_local()[source]¶ Set the code as a ‘local’ code, meaning that all the files belonging to the code will be copied to the cluster, and the file set with set_exec_filename will be run.
It also deletes the flags related to the local case (if any)
-
_set_remote()[source]¶ Set the code as a ‘remote’ code, meaning that the code itself has no files attached, but only a location on a remote computer (with an absolute path of the executable on the remote computer).
It also deletes the flags related to the local case (if any)
-
_validate()[source]¶ Perform validation of the Data object.
Note
validation of data source checks license and requires attribution to be provided in field ‘description’ of source in the case of any CC-BY* license. If such requirement is too strict, one can remove/comment it out.
-
can_run_on(computer)[source]¶ Return True if this code can run on the given computer, False otherwise.
Local codes can run on any machine; remote codes can run only on the machine on which they reside.
TODO: add filters to mask the remote machines on which a local code can run.
-
full_label¶ Get full label of this code.
Returns label of the form <code-label>@<computer-name>.
-
full_text_info(verbose=False)[source]¶ Return a (multiline) string with a human-readable detailed information on this computer
-
classmethod
get(pk=None, label=None, machinename=None)[source]¶ Get a Computer object with given identifier string, that can either be the numeric ID (pk), or the label (and computername) (if unique).
Parameters: - pk – the numeric ID (pk) for code
- label – the code label identifying the code to load
- machinename – the machine name where code is setup
Raises: - aiida.common.NotExistent – if no code identified by the given string is found
- aiida.common.MultipleObjectsError – if the string cannot identify uniquely a code
- aiida.common.InputValidationError – if neither a pk nor a label was passed in
-
get_append_text()[source]¶ Return the postexec_code, or an empty string if no post-exec code was defined.
-
get_builder()[source]¶ Create and return a new ProcessBuilder for the default Calculation plugin, as obtained by the self.get_input_plugin_name() method.
Note: it also sets the
builder.codevalue.Raises: - aiida.common.MissingPluginError – if the specified plugin does not exist.
- ValueError – if no default plugin was specified.
Returns:
-
classmethod
get_code_helper(label, machinename=None)[source]¶ Parameters: - label – the code label identifying the code to load
- machinename – the machine name where code is setup
Raises: - aiida.common.NotExistent – if no code identified by the given string is found
- aiida.common.MultipleObjectsError – if the string cannot identify uniquely a code
-
get_description()[source]¶ Return a string description of this Code instance.
Returns: string description of this Code instance
-
get_execname()[source]¶ Return the executable string to be put in the script. For local codes, it is ./LOCAL_EXECUTABLE_NAME For remote codes, it is the absolute path to the executable.
-
classmethod
get_from_string(code_string)[source]¶ Get a Computer object with given identifier string in the format label@machinename. See the note below for details on the string detection algorithm.
Note
the (leftmost) ‘@’ symbol is always used to split code and computername. Therefore do not use ‘@’ in the code name if you want to use this function (‘@’ in the computer name are instead valid).
Parameters: code_string – the code string identifying the code to load
Raises: - aiida.common.NotExistent – if no code identified by the given string is found
- aiida.common.MultipleObjectsError – if the string cannot identify uniquely a code
- aiida.common.InputValidationError – if code_string is not of string type
-
get_full_text_info(verbose=False)[source]¶ Return a (multiline) string with a human-readable detailed information on this computer
-
get_input_plugin_name()[source]¶ Return the name of the default input plugin (or None if no input plugin was set.
-
get_prepend_text()[source]¶ Return the code that will be put in the scheduler script before the execution, or an empty string if no pre-exec code was defined.
Determines whether the Code is hidden or not
-
is_local()[source]¶ Return True if the code is ‘local’, False if it is ‘remote’ (see also documentation of the set_local and set_remote functions).
-
classmethod
list_for_plugin(plugin, labels=True)[source]¶ Return a list of valid code strings for a given plugin.
Parameters: - plugin – The string of the plugin.
- labels – if True, return a list of code names, otherwise return the code PKs (integers).
Returns: a list of string, with the code names if labels is True, otherwise a list of integers with the code PKs.
-
relabel(new_label, raise_error=True)[source]¶ Relabel this code.
Parameters: - new_label – new code label
- raise_error – Set to False in order to return a list of errors instead of raising them.
-
reveal()[source]¶ Reveal the code (allows to show it in the verdi code list) By default, it is revealed
-
set_append_text(code)[source]¶ Pass a string of code that will be put in the scheduler script after the execution of the code.
-
set_files(files)[source]¶ Given a list of filenames (or a single filename string), add it to the path (all at level zero, i.e. without folders). Therefore, be careful for files with the same name!
Todo: decide whether to check if the Code must be a local executable to be able to call this function.
-
set_input_plugin_name(input_plugin)[source]¶ Set the name of the default input plugin, to be used for the automatic generation of a new calculation.
-
set_local_executable(exec_name)[source]¶ Set the filename of the local executable. Implicitly set the code as local.
-
set_prepend_text(code)[source]¶ Pass a string of code that will be put in the scheduler script before the execution of the code.
-
set_remote_computer_exec(remote_computer_exec)[source]¶ Set the code as remote, and pass the computer on which it resides and the absolute path on that computer.
Parameters: remote_computer_exec – a tuple (computer, remote_exec_path), where computer is a aiida.orm.Computer and remote_exec_path is the absolute path of the main executable on remote computer.
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.Float(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.numeric.NumericTypeData sub class to represent a float value.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.float'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.float.Float.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.float.'¶
-
_type¶ alias of
__builtin__.float
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.FolderData(backend=None, user=None, computer=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.DataData sub class to represent a folder on a file system.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.folder'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.folder.FolderData.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.folder.'¶
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.Int(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.numeric.NumericTypeData sub class to represent an integer value.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.int'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.int.Int.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.int.'¶
-
_type¶ alias of
__builtin__.int
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.List(**kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.Data,_abcoll.MutableSequenceData sub class to represent a list.
-
_LIST_KEY= 'list'¶
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(**kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.list'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 102¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.list.List.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.list.'¶
-
_using_list_reference()[source]¶ This function tells the class if we are using a list reference. This means that calls to self.get_list return a reference rather than a copy of the underlying list and therefore self.set_list need not be called. This knwoledge is essential to make sure this class is performant.
Currently the implementation assumes that if the node needs to be stored then it is using the attributes cache which is a reference.
Returns: True if using self.get_list returns a reference to the underlying sequence. False otherwise. Return type: bool
-
index(value) → integer -- return first index of value.[source]¶ Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
-
pop([index]) → item -- remove and return item at index (default last).[source]¶ Raise IndexError if list is empty or index is out of range.
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.OrbitalData(backend=None, user=None, computer=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.DataUsed for storing collections of orbitals, as well as providing methods for accessing them internally.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.orbital'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_get_orbital_class_from_orbital_dict(orbital_dict)[source]¶ Gets the orbital class from the orbital dictionary stored in DB
Parameters: orbital_dict – orbital dictionary associated with the orbital Returns: an Orbital produced using the module_name
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.orbital.OrbitalData.'¶
-
static
_prep_orbital_dict_keys_from_site(site)[source]¶ Prepares the position from an input site.
Parameters: site – a site of site class Return out_dict: a dictionary of attributes parsed from the site (currently only position)
-
_query_type_string= 'data.orbital.'¶
-
clear_orbitals()[source]¶ Remove all orbitals that were added to the class Cannot work if OrbitalData has been already stored
-
get_orbitals(with_tags=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Returns all orbitals by default. If a site is provided, returns all orbitals cooresponding to the location of that site, additional arguments may be provided, which act as filters on the retrieved orbitals.
Parameters: - site – if provided, returns all orbitals with position of site
- with_tags – if provided returns all tags stored
Kwargs: attributes than can filter the set of returned orbitals
Return list_of_outputs: a list of orbitals and also tags if with_tags was set to True
-
set_orbitals(orbital, tag=None)[source]¶ Sets the orbitals into the database. Uses the orbital’s inherent set_orbital_dict method to generate a orbital dict string at is stored along with the tags, if provided.
Parameters: - orbital – an orbital or list of orbitals to be set
- tag – a list of strings must be of length orbital
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.Dict(**kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.DataData sub class to represent a dictionary.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(**kwargs)[source]¶ Store a dictionary as a Node instance.
Usual rules for attribute names apply, in particular, keys cannot start with an underscore, or a ValueError will be raised.
Initial attributes can be changed, deleted or added as long as the node is not stored.
Parameters: dict – the dictionary to set
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.dict'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.dict.Dict.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.dict.'¶
-
dict¶ Return an instance of AttributeManager that transforms the dictionary into an attribute dict.
Note
this will allow one to do node.dict.key as well as node.dict[key].
Returns: an instance of the AttributeResultManager.
-
keys()[source]¶ Iterator of valid keys stored in the Dict object.
Returns: iterator over the keys of the current dictionary
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.RemoteData(remote_path=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.DataStore a link to a file or folder on a remote machine.
Remember to pass a computer!
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(remote_path=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.remote'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.remote.RemoteData.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.remote.'¶
-
_validate()[source]¶ Perform validation of the Data object.
Note
validation of data source checks license and requires attribution to be provided in field ‘description’ of source in the case of any CC-BY* license. If such requirement is too strict, one can remove/comment it out.
-
getfile(relpath, destpath)[source]¶ Connects to the remote folder and gets a string with the (full) content of the file.
Parameters: - relpath – The relative path of the file to show.
- destpath – A path on the local computer to get the file
Returns: a string with the file content
-
is_empty¶ Check if remote folder is empty
-
listdir(relpath='.')[source]¶ Connects to the remote folder and lists the directory content.
Parameters: relpath – If ‘relpath’ is specified, lists the content of the given subfolder. Returns: a flat list of file/directory names (as strings).
-
listdir_withattributes(path='.')[source]¶ Connects to the remote folder and lists the directory content.
Parameters: relpath – If ‘relpath’ is specified, lists the content of the given subfolder. Returns: a list of dictionaries, where the documentation is in :py:class:Transport.listdir_withattributes.
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.SinglefileData(filepath, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.DataData class that can be used to store a single file in its repository.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(filepath, **kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.singlefile'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.singlefile.SinglefileData.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.singlefile.'¶
-
_validate()[source]¶ Ensure that there is one object stored in the repository, whose key matches value set for filename attr.
-
filename¶ Return the name of the file stored.
Returns: the filename under which the file is stored in the repository
-
get_content()[source]¶ Return the content of the single file stored for this data node.
Returns: the string content of the file
-
open(key=None, mode='r')[source]¶ Return an open file handle to the content of this data node.
Parameters: - key – optional key within the repository, by default is the filename set in the attributes
- mode – the mode with which to open the file handle
Returns: a file handle in read mode
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.Str(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.base.BaseTypeData sub class to represent a string value.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.str'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.str.Str.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.str.'¶
-
_type¶ alias of
__builtin__.str
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.StructureData(cell=None, pbc=None, ase=None, pymatgen=None, pymatgen_structure=None, pymatgen_molecule=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.DataThis class contains the information about a given structure, i.e. a collection of sites together with a cell, the boundary conditions (whether they are periodic or not) and other related useful information.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(cell=None, pbc=None, ase=None, pymatgen=None, pymatgen_structure=None, pymatgen_molecule=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_adjust_default_cell(vacuum_factor=1.0, vacuum_addition=10.0, pbc=(False, False, False))[source]¶ If the structure was imported from an xyz file, it lacks a defined cell, and the default cell is taken ([[1,0,0], [0,1,0], [0,0,1]]), leading to an unphysical definition of the structure. This method will adjust the cell
-
_dimensionality_label= {0: '', 1: 'length', 2: 'surface', 3: 'volume'}¶
-
_get_cif(converter='ase', store=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Creates
aiida.orm.nodes.data.cif.CifData.Parameters: - converter – specify the converter. Default ‘ase’.
- store – If True, intermediate calculation gets stored in the AiiDA database for record. Default False.
Returns:
-
_get_object_ase()[source]¶ Converts
StructureDatato ase.AtomsReturns: an ase.Atoms object
-
_get_object_phonopyatoms()[source]¶ Converts StructureData to PhonopyAtoms
Returns: a PhonopyAtoms object
-
_get_object_pymatgen(**kwargs)[source]¶ Converts
StructureDatato pymatgen objectReturns: a pymatgen Structure for structures with periodic boundary conditions (in three dimensions) and Molecule otherwise Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.0.13, usage of earlier versions may cause errors).
-
_get_object_pymatgen_molecule(**kwargs)[source]¶ Converts
StructureDatato pymatgen Molecule objectReturns: a pymatgen Molecule object corresponding to this StructureDataobject.Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.0.13, usage of earlier versions may cause errors)
-
_get_object_pymatgen_structure(**kwargs)[source]¶ Converts
StructureDatato pymatgen Structure object :param add_spin: True to add the spins to the pymatgen structure. Default is False (no spin added).Note
The spins are set according to the following rule:
- if the kind name ends with 1 -> spin=+1
- if the kind name ends with 2 -> spin=-1
Returns: a pymatgen Structure object corresponding to this StructureDataobjectRaises: ValueError – if periodic boundary conditions does not hold in at least one dimension of real space; if there are partial occupancies together with spins (defined by kind names ending with ‘1’ or ‘2’). Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.0.13, usage of earlier versions may cause errors)
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.structure.StructureData.'¶
-
_prepare_chemdoodle(main_file_name='')[source]¶ Write the given structure to a string of format required by ChemDoodle.
-
_prepare_tcod(main_file_name='', **kwargs)[source]¶ Write the given structure to a string of format TCOD CIF.
-
_prepare_xsf(main_file_name='')[source]¶ Write the given structure to a string of format XSF (for XCrySDen).
-
_query_type_string= 'data.structure.'¶
-
_set_incompatibilities= [('ase', 'cell'), ('ase', 'pbc'), ('ase', 'pymatgen'), ('ase', 'pymatgen_molecule'), ('ase', 'pymatgen_structure'), ('cell', 'pymatgen'), ('cell', 'pymatgen_molecule'), ('cell', 'pymatgen_structure'), ('pbc', 'pymatgen'), ('pbc', 'pymatgen_molecule'), ('pbc', 'pymatgen_structure'), ('pymatgen', 'pymatgen_molecule'), ('pymatgen', 'pymatgen_structure'), ('pymatgen_molecule', 'pymatgen_structure')]¶
-
append_atom(**kwargs)[source]¶ Append an atom to the Structure, taking care of creating the corresponding kind.
Parameters: - ase – the ase Atom object from which we want to create a new atom (if present, this must be the only parameter)
- position – the position of the atom (three numbers in angstrom)
- symbols – passed to the constructor of the Kind object.
- weights – passed to the constructor of the Kind object.
- name – passed to the constructor of the Kind object. See also the note below.
Note
Note on the ‘name’ parameter (that is, the name of the kind):
- if specified, no checks are done on existing species. Simply, a new kind with that name is created. If there is a name clash, a check is done: if the kinds are identical, no error is issued; otherwise, an error is issued because you are trying to store two different kinds with the same name.
- if not specified, the name is automatically generated. Before adding the kind, a check is done. If other species with the same properties already exist, no new kinds are created, but the site is added to the existing (identical) kind. (Actually, the first kind that is encountered). Otherwise, the name is made unique first, by adding to the string containing the list of chemical symbols a number starting from 1, until an unique name is found
Note
checks of equality of species are done using the
compare_with()method.
-
append_kind(kind)[source]¶ Append a kind to the
StructureData. It makes a copy of the kind.Parameters: kind – the site to append, must be a Kind object.
-
append_site(site)[source]¶ Append a site to the
StructureData. It makes a copy of the site.Parameters: site – the site to append. It must be a Site object.
-
cell¶ Returns the cell shape.
Returns: a 3x3 list of lists.
-
cell_angles¶ Get the angles between the cell lattice vectors in degrees.
-
cell_lengths¶ Get the lengths of cell lattice vectors in angstroms.
-
get_ase()[source]¶ Get the ASE object. Requires to be able to import ase.
Returns: an ASE object corresponding to this StructureDataobject.Note
If any site is an alloy or has vacancies, a ValueError is raised (from the site.get_ase() routine).
-
get_cif(converter='ase', store=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Creates
aiida.orm.nodes.data.cif.CifData.New in version 1.0: Renamed from _get_cif
Parameters: - converter – specify the converter. Default ‘ase’.
- store – If True, intermediate calculation gets stored in the AiiDA database for record. Default False.
Returns:
-
get_composition()[source]¶ Returns the chemical composition of this structure as a dictionary, where each key is the kind symbol (e.g. H, Li, Ba), and each value is the number of occurences of that element in this structure. For BaZrO3 it would return {‘Ba’:1, ‘Zr’:1, ‘O’:3}. No reduction with smallest common divisor!
Returns: a dictionary with the composition
-
get_description()[source]¶ Returns a string with infos retrieved from StructureData node’s properties
Parameters: self – the StructureData node Returns: retsrt: the description string
-
get_dimensionality()[source]¶ This function checks the dimensionality of the structure and calculates its length/surface/volume :return: returns the dimensionality and length/surface/volume
-
get_formula(mode='hill', separator='')[source]¶ Return a string with the chemical formula.
Parameters: - mode –
a string to specify how to generate the formula, can assume one of the following values:
- ’hill’ (default): count the number of atoms of each species,
then use Hill notation, i.e. alphabetical order with C and H
first if one or several C atom(s) is (are) present, e.g.
['C','H','H','H','O','C','H','H','H']will return'C2H6O'['S','O','O','H','O','H','O']will return'H2O4S'From E. A. Hill, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 22 (8), pp 478–494 (1900) - ’hill_compact’: same as hill but the number of atoms for each
species is divided by the greatest common divisor of all of them, e.g.
['C','H','H','H','O','C','H','H','H','O','O','O']will return'CH3O2' - ’reduce’: group repeated symbols e.g.
['Ba', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O', 'Ba', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O', 'Ba', 'Ti', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O']will return'BaTiO3BaTiO3BaTi2O3' - ’group’: will try to group as much as possible parts of the formula
e.g.
['Ba', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O', 'Ba', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O', 'Ba', 'Ti', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O']will return'(BaTiO3)2BaTi2O3' - ’count’: same as hill (i.e. one just counts the number
of atoms of each species) without the re-ordering (take the
order of the atomic sites), e.g.
['Ba', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O','Ba', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O']will return'Ba2Ti2O6' - ’count_compact’: same as count but the number of atoms
for each species is divided by the greatest common divisor of
all of them, e.g.
['Ba', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O','Ba', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O']will return'BaTiO3'
- ’hill’ (default): count the number of atoms of each species,
then use Hill notation, i.e. alphabetical order with C and H
first if one or several C atom(s) is (are) present, e.g.
- separator – a string used to concatenate symbols. Default empty.
Returns: a string with the formula
Note
in modes reduce, group, count and count_compact, the initial order in which the atoms were appended by the user is used to group and/or order the symbols in the formula
- mode –
-
get_kind(kind_name)[source]¶ Return the kind object associated with the given kind name.
Parameters: kind_name – String, the name of the kind you want to get Returns: The Kind object associated with the given kind_name, if a Kind with the given name is present in the structure. Raise: ValueError if the kind_name is not present.
-
get_kind_names()[source]¶ Return a list of kind names (in the same order of the
self.kindsproperty, but return the names rather than Kind objects)Note
This is NOT necessarily a list of chemical symbols! Use get_symbols_set for chemical symbols
Returns: a list of strings.
-
get_pymatgen(**kwargs)[source]¶ Get pymatgen object. Returns Structure for structures with periodic boundary conditions (in three dimensions) and Molecule otherwise. :param add_spin: True to add the spins to the pymatgen structure. Default is False (no spin added).
Note
The spins are set according to the following rule:
- if the kind name ends with 1 -> spin=+1
- if the kind name ends with 2 -> spin=-1
Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.0.13, usage of earlier versions may cause errors).
-
get_pymatgen_molecule()[source]¶ Get the pymatgen Molecule object.
Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.0.13, usage of earlier versions may cause errors).
Returns: a pymatgen Molecule object corresponding to this StructureDataobject.
-
get_pymatgen_structure(**kwargs)[source]¶ Get the pymatgen Structure object. :param add_spin: True to add the spins to the pymatgen structure. Default is False (no spin added).
Note
The spins are set according to the following rule:
- if the kind name ends with 1 -> spin=+1
- if the kind name ends with 2 -> spin=-1
Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.0.13, usage of earlier versions may cause errors).
Returns: a pymatgen Structure object corresponding to this StructureDataobject.Raises: ValueError – if periodic boundary conditions do not hold in at least one dimension of real space.
-
get_site_kindnames()[source]¶ Return a list with length equal to the number of sites of this structure, where each element of the list is the kind name of the corresponding site.
Note
This is NOT necessarily a list of chemical symbols! Use
[ self.get_kind(s.kind_name).get_symbols_string() for s in self.sites]for chemical symbolsReturns: a list of strings
-
get_symbols_set()[source]¶ Return a set containing the names of all elements involved in this structure (i.e., for it joins the list of symbols for each kind k in the structure).
Returns: a set of strings of element names.
-
has_vacancies¶ Return whether the structure has vacancies in the structure.
Returns: a boolean, True if at least one kind has a vacancy
-
is_alloy¶ Return whether the structure contains any alloy kinds.
Returns: a boolean, True if at least one kind is an alloy
-
kinds¶ Returns a list of kinds.
-
pbc¶ Get the periodic boundary conditions.
Returns: a tuple of three booleans, each one tells if there are periodic boundary conditions for the i-th real-space direction (i=1,2,3)
-
reset_cell(new_cell)[source]¶ Reset the cell of a structure not yet stored to a new value.
Parameters: new_cell – list specifying the cell vectors Raises: ModificationNotAllowed: if object is already stored
-
reset_sites_positions(new_positions, conserve_particle=True)[source]¶ Replace all the Site positions attached to the Structure
Parameters: - new_positions – list of (3D) positions for every sites.
- conserve_particle – if True, allows the possibility of removing a site. currently not implemented.
Raises: - aiida.common.ModificationNotAllowed – if object is stored already
- ValueError – if positions are invalid
Note
it is assumed that the order of the new_positions is given in the same order of the one it’s substituting, i.e. the kind of the site will not be checked.
-
set_pymatgen(obj, **kwargs)[source]¶ Load the structure from a pymatgen object.
Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.0.13, usage of earlier versions may cause errors).
-
set_pymatgen_molecule(mol, margin=5)[source]¶ Load the structure from a pymatgen Molecule object.
Parameters: margin – the margin to be added in all directions of the bounding box of the molecule. Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.0.13, usage of earlier versions may cause errors).
-
set_pymatgen_structure(struct)[source]¶ Load the structure from a pymatgen Structure object.
Note
periodic boundary conditions are set to True in all three directions.
Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.3.5, usage of earlier versions may cause errors).
Raises: ValueError – if there are partial occupancies together with spins.
-
sites¶ Returns a list of sites.
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.UpfData(filepath=None, source=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.singlefile.SinglefileDataFunction not yet documented.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(filepath=None, source=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.upf'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.upf.UpfData.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.upf.'¶
-
_validate()[source]¶ Ensure that there is one object stored in the repository, whose key matches value set for filename attr.
-
element¶
-
classmethod
from_md5(md5)[source]¶ Return a list of all UPF pseudopotentials that match a given MD5 hash.
Note that the hash has to be stored in a _md5 attribute, otherwise the pseudo will not be found.
-
classmethod
get_or_create(filepath, use_first=False, store_upf=True)[source]¶ Pass the same parameter of the init; if a file with the same md5 is found, that UpfData is returned.
Parameters: - filepath – an absolute filepath on disk
- use_first – if False (default), raise an exception if more than one potential is found. If it is True, instead, use the first available pseudopotential.
- store_upf (bool) – If false, the UpfData objects are not stored in the database. default=True.
Return (upf, created): where upf is the UpfData object, and create is either True if the object was created, or False if the object was retrieved from the DB.
-
classmethod
get_upf_groups(filter_elements=None, user=None)[source]¶ Return all names of groups of type UpfFamily, possibly with some filters.
Parameters: - filter_elements – A string or a list of strings. If present, returns only the groups that contains one Upf for every element present in the list. Default=None, meaning that all families are returned.
- user – if None (default), return the groups for all users. If defined, it should be either a DbUser instance, or a string for the username (that is, the user email).
-
md5sum¶
-
store(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Store the node, reparsing the file so that the md5 and the element are correctly reset.
-
upffamily_type_string= 'data.upf'¶
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.NumericType(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.base.BaseTypeSub class of Data to store numbers, overloading common operators (
+,*, …).-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.numeric'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.numeric.NumericType.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.numeric.'¶
-
Subpackages¶
Submodules¶
Data sub class to be used as a base for data containers that represent base python data types.
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.base.BaseType(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.DataData sub class to be used as a base for data containers that represent base python data types.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.base'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.base.BaseType.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.base.'¶
-
value¶
-
-
aiida.orm.nodes.data.base.to_aiida_type(*args, **kw)[source]¶ Turns basic Python types (str, int, float, bool) into the corresponding AiiDA types.
Data sub class to represent a boolean value.
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.bool.Bool(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.base.BaseTypeData sub class to represent a boolean value.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.bool'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.bool.Bool.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.bool.'¶
-
_type¶ alias of
__builtin__.bool
-
Tools for handling Crystallographic Information Files (CIF)
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.cif.CifData(ase=None, filepath=None, values=None, source=None, scan_type='standard', parse_policy='eager', **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.singlefile.SinglefileDataWrapper for Crystallographic Interchange File (CIF)
Note
the filepath (physical) is held as the authoritative source of information, so all conversions are done through the physical file: when setting
aseorvalues, a physical CIF file is generated first, the values are updated from the physical CIF file.-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(ase=None, filepath=None, values=None, source=None, scan_type='standard', parse_policy='eager', **kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.cif'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_ase= None¶
-
_get_aiida_structure(converter='pymatgen', store=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Creates
aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure.StructureData.Parameters: - converter – specify the converter. Default ‘pymatgen’.
- store – if True, intermediate calculation gets stored in the AiiDA database for record. Default False.
- primitive_cell – if True, primitive cell is returned, conventional cell if False. Default False.
- occupancy_tolerance – If total occupancy of a site is between 1 and occupancy_tolerance, the occupancies will be scaled down to 1. (pymatgen only)
- site_tolerance – This tolerance is used to determine if two sites are sitting in the same position, in which case they will be combined to a single disordered site. Defaults to 1e-4. (pymatgen only)
Returns:
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_parse_policies= ('eager', 'lazy')¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.cif.CifData.'¶
-
_prepare_cif(main_file_name='')[source]¶ Return CIF string of CifData object.
If parsed values are present, a CIF string is created and written to file. If no parsed values are present, the CIF string is read from file.
-
_prepare_tcod(main_file_name='', **kwargs)[source]¶ Write the given CIF to a string of format TCOD CIF.
-
_query_type_string= 'data.cif.'¶
-
_scan_types= ('standard', 'flex')¶
-
_set_incompatibilities= [('ase', 'filepath'), ('ase', 'values'), ('filepath', 'values')]¶
-
_values= None¶
-
ase¶ ASE object, representing the CIF.
Note
requires ASE module.
-
classmethod
from_md5(md5)[source]¶ Return a list of all CIF files that match a given MD5 hash.
Note
the hash has to be stored in a
_md5attribute, otherwise the CIF file will not be found.
-
get_ase(**kwargs)[source]¶ Returns ASE object, representing the CIF. This function differs from the property
aseby the possibility to pass the keyworded arguments (kwargs) to ase.io.cif.read_cif().Note
requires ASE module.
-
get_formulae(mode='sum')[source]¶ Return chemical formulae specified in CIF file.
Note: This does not compute the formula, it only reads it from the appropriate tag. Use refine_inline to compute formulae.
-
classmethod
get_or_create(filename, use_first=False, store_cif=True)[source]¶ Pass the same parameter of the init; if a file with the same md5 is found, that CifData is returned.
Parameters: - filename – an absolute filename on disk
- use_first – if False (default), raise an exception if more than one CIF file is found. If it is True, instead, use the first available CIF file.
- store_cif (bool) – If false, the CifData objects are not stored in the database. default=True.
Return (cif, created): where cif is the CifData object, and create is either True if the object was created, or False if the object was retrieved from the DB.
-
get_structure(converter='pymatgen', store=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Creates
aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure.StructureData.New in version 1.0: Renamed from _get_aiida_structure
Parameters: - converter – specify the converter. Default ‘pymatgen’.
- store – if True, intermediate calculation gets stored in the AiiDA database for record. Default False.
- primitive_cell – if True, primitive cell is returned, conventional cell if False. Default False.
- occupancy_tolerance – If total occupancy of a site is between 1 and occupancy_tolerance, the occupancies will be scaled down to 1. (pymatgen only)
- site_tolerance – This tolerance is used to determine if two sites are sitting in the same position, in which case they will be combined to a single disordered site. Defaults to 1e-4. (pymatgen only)
Returns:
-
has_atomic_sites¶ Returns whether there are any atomic sites defined in the cif data. That is to say, it will check all the values for the _atom_site_fract_* tags and if they are all equal to ? that means there are no relevant atomic sites defined and the function will return False. In all other cases the function will return True
Returns: False when at least one atomic site fractional coordinate is not equal to ? and True otherwise
-
has_attached_hydrogens¶ Check if there are hydrogens without coordinates, specified as attached to the atoms of the structure.
Returns: True if there are attached hydrogens, False otherwise.
-
has_partial_occupancies¶ Return if the cif data contains partial occupancies
A partial occupancy is defined as site with an occupancy that differs from unity, within a precision of 1E-6
Returns: True if there are partial occupancies, False otherwise
-
has_undefined_atomic_sites¶ Return whether the cif data contains any undefined atomic sites.
An undefined atomic site is defined as a site where at least one of the fractional coordinates specified in the _atom_site_fract_* tags, cannot be successfully interpreted as a float. If the cif data contains any site that matches this description, or it does not contain any atomic site tags at all, the cif data is said to have undefined atomic sites.
Returns: boolean, True if no atomic sites are defined or if any of the defined sites contain undefined positions and False otherwise
-
has_unknown_species¶ Returns whether the cif contains atomic species that are not recognized by AiiDA.
The known species are taken from the elements dictionary in aiida.common.constants, with the exception of the “unknown” placeholder element with symbol ‘X’, as this could not be used to construct a real structure. If any of the formula of the cif data contain species that are not in that elements dictionary, the function will return True and False in all other cases. If there is no formulae to be found, it will return None
Returns: True when there are unknown species in any of the formulae, False if not, None if no formula found
-
parse(scan_type=None)[source]¶ Parses CIF file and sets attributes.
Parameters: scan_type – See set_scan_type
-
put_object_from_file(path, key=None, mode='w', encoding='utf8', force=False)[source]¶ Set the file.
If the source is set and the MD5 checksum of new file is different from the source, the source has to be deleted.
-
static
read_cif(fileobj, index=-1, **kwargs)[source]¶ A wrapper method that simulates the behavior of the old function ase.io.cif.read_cif by using the new generic ase.io.read function.
-
set_ase(aseatoms)[source]¶ Set the contents of the CifData starting from an ASE atoms object
Parameters: aseatoms – the ASE atoms object
-
set_parse_policy(parse_policy)[source]¶ Set the parse policy.
Parameters: parse_policy – Either ‘eager’ (parse CIF file on set_file) or ‘lazy’ (defer parsing until needed)
-
set_scan_type(scan_type)[source]¶ Set the scan_type for PyCifRW.
The ‘flex’ scan_type of PyCifRW is faster for large CIF files but does not yet support the CIF2 format as of 02/2018. See the CifFile.ReadCif function
Parameters: scan_type – Either ‘standard’ or ‘flex’ (see _scan_types)
-
set_values(values)[source]¶ Set internal representation to values.
Warning: This also writes a new CIF file.
Parameters: values – PyCifRW CifFile object Note
requires PyCifRW module.
-
values¶ PyCifRW structure, representing the CIF datablocks.
Note
requires PyCifRW module.
-
-
aiida.orm.nodes.data.cif.cif_from_ase(ase, full_occupancies=False, add_fake_biso=False)[source]¶ Construct a CIF datablock from the ASE structure. The code is taken from https://wiki.fysik.dtu.dk/ase/epydoc/ase.io.cif-pysrc.html#write_cif, as the original ASE code contains a bug in printing the Hermann-Mauguin symmetry space group symbol.
Parameters: ase – ASE “images” Returns: array of CIF datablocks
-
aiida.orm.nodes.data.cif.has_pycifrw()[source]¶ Returns: True if the PyCifRW module can be imported, False otherwise.
-
aiida.orm.nodes.data.cif.parse_formula(formula)[source]¶ Parses the Hill formulae, written with spaces for separators.
-
aiida.orm.nodes.data.cif.pycifrw_from_cif(datablocks, loops=None, names=None)[source]¶ Constructs PyCifRW’s CifFile from an array of CIF datablocks.
Parameters: - datablocks – an array of CIF datablocks
- loops – optional dict of lists of CIF tag loops.
- names – optional list of datablock names
Returns: CifFile
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.code.Code(remote_computer_exec=None, local_executable=None, input_plugin_name=None, files=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.DataA code entity. It can either be ‘local’, or ‘remote’.
- Local code: it is a collection of files/dirs (added using the add_path() method), where one file is flagged as executable (using the set_local_executable() method).
- Remote code: it is a pair (remotecomputer, remotepath_of_executable) set using the set_remote_computer_exec() method.
For both codes, one can set some code to be executed right before or right after the execution of the code, using the set_preexec_code() and set_postexec_code() methods (e.g., the set_preexec_code() can be used to load specific modules required for the code to be run).
-
HIDDEN_KEY= 'hidden'¶
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(remote_computer_exec=None, local_executable=None, input_plugin_name=None, files=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.code'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.code.Code.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.code.'¶
-
_set_local()[source]¶ Set the code as a ‘local’ code, meaning that all the files belonging to the code will be copied to the cluster, and the file set with set_exec_filename will be run.
It also deletes the flags related to the local case (if any)
-
_set_remote()[source]¶ Set the code as a ‘remote’ code, meaning that the code itself has no files attached, but only a location on a remote computer (with an absolute path of the executable on the remote computer).
It also deletes the flags related to the local case (if any)
-
_validate()[source]¶ Perform validation of the Data object.
Note
validation of data source checks license and requires attribution to be provided in field ‘description’ of source in the case of any CC-BY* license. If such requirement is too strict, one can remove/comment it out.
-
can_run_on(computer)[source]¶ Return True if this code can run on the given computer, False otherwise.
Local codes can run on any machine; remote codes can run only on the machine on which they reside.
TODO: add filters to mask the remote machines on which a local code can run.
-
full_label¶ Get full label of this code.
Returns label of the form <code-label>@<computer-name>.
-
full_text_info(verbose=False)[source]¶ Return a (multiline) string with a human-readable detailed information on this computer
-
classmethod
get(pk=None, label=None, machinename=None)[source]¶ Get a Computer object with given identifier string, that can either be the numeric ID (pk), or the label (and computername) (if unique).
Parameters: - pk – the numeric ID (pk) for code
- label – the code label identifying the code to load
- machinename – the machine name where code is setup
Raises: - aiida.common.NotExistent – if no code identified by the given string is found
- aiida.common.MultipleObjectsError – if the string cannot identify uniquely a code
- aiida.common.InputValidationError – if neither a pk nor a label was passed in
-
get_append_text()[source]¶ Return the postexec_code, or an empty string if no post-exec code was defined.
-
get_builder()[source]¶ Create and return a new ProcessBuilder for the default Calculation plugin, as obtained by the self.get_input_plugin_name() method.
Note: it also sets the
builder.codevalue.Raises: - aiida.common.MissingPluginError – if the specified plugin does not exist.
- ValueError – if no default plugin was specified.
Returns:
-
classmethod
get_code_helper(label, machinename=None)[source]¶ Parameters: - label – the code label identifying the code to load
- machinename – the machine name where code is setup
Raises: - aiida.common.NotExistent – if no code identified by the given string is found
- aiida.common.MultipleObjectsError – if the string cannot identify uniquely a code
-
get_description()[source]¶ Return a string description of this Code instance.
Returns: string description of this Code instance
-
get_execname()[source]¶ Return the executable string to be put in the script. For local codes, it is ./LOCAL_EXECUTABLE_NAME For remote codes, it is the absolute path to the executable.
-
classmethod
get_from_string(code_string)[source]¶ Get a Computer object with given identifier string in the format label@machinename. See the note below for details on the string detection algorithm.
Note
the (leftmost) ‘@’ symbol is always used to split code and computername. Therefore do not use ‘@’ in the code name if you want to use this function (‘@’ in the computer name are instead valid).
Parameters: code_string – the code string identifying the code to load
Raises: - aiida.common.NotExistent – if no code identified by the given string is found
- aiida.common.MultipleObjectsError – if the string cannot identify uniquely a code
- aiida.common.InputValidationError – if code_string is not of string type
-
get_full_text_info(verbose=False)[source]¶ Return a (multiline) string with a human-readable detailed information on this computer
-
get_input_plugin_name()[source]¶ Return the name of the default input plugin (or None if no input plugin was set.
-
get_prepend_text()[source]¶ Return the code that will be put in the scheduler script before the execution, or an empty string if no pre-exec code was defined.
Determines whether the Code is hidden or not
-
is_local()[source]¶ Return True if the code is ‘local’, False if it is ‘remote’ (see also documentation of the set_local and set_remote functions).
-
classmethod
list_for_plugin(plugin, labels=True)[source]¶ Return a list of valid code strings for a given plugin.
Parameters: - plugin – The string of the plugin.
- labels – if True, return a list of code names, otherwise return the code PKs (integers).
Returns: a list of string, with the code names if labels is True, otherwise a list of integers with the code PKs.
-
relabel(new_label, raise_error=True)[source]¶ Relabel this code.
Parameters: - new_label – new code label
- raise_error – Set to False in order to return a list of errors instead of raising them.
-
reveal()[source]¶ Reveal the code (allows to show it in the verdi code list) By default, it is revealed
-
set_append_text(code)[source]¶ Pass a string of code that will be put in the scheduler script after the execution of the code.
-
set_files(files)[source]¶ Given a list of filenames (or a single filename string), add it to the path (all at level zero, i.e. without folders). Therefore, be careful for files with the same name!
Todo: decide whether to check if the Code must be a local executable to be able to call this function.
-
set_input_plugin_name(input_plugin)[source]¶ Set the name of the default input plugin, to be used for the automatic generation of a new calculation.
-
set_local_executable(exec_name)[source]¶ Set the filename of the local executable. Implicitly set the code as local.
-
set_prepend_text(code)[source]¶ Pass a string of code that will be put in the scheduler script before the execution of the code.
-
set_remote_computer_exec(remote_computer_exec)[source]¶ Set the code as remote, and pass the computer on which it resides and the absolute path on that computer.
Parameters: remote_computer_exec – a tuple (computer, remote_exec_path), where computer is a aiida.orm.Computer and remote_exec_path is the absolute path of the main executable on remote computer.
Module with Node sub class Data to be used as a base class for data structures.
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.Data(backend=None, user=None, computer=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.node.NodeThis class is base class for all data objects.
Specifications of the Data class: AiiDA Data objects are subclasses of Node and should have
Multiple inheritance must be supported, i.e. Data should have methods for querying and be able to inherit other library objects such as ASE for structures.
Architecture note: The code plugin is responsible for converting a raw data object produced by code to AiiDA standard object format. The data object then validates itself according to its method. This is done independently in order to allow cross-validation of plugins.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__deepcopy__(memo)[source]¶ Create a clone of the Data node by pipiong through to the clone method and return the result.
Returns: an unstored clone of this Data node
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.data'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_export_format_replacements= {}¶
-
_exportcontent(fileformat, main_file_name='', **kwargs)[source]¶ Converts a Data node to one (or multiple) files.
Note: Export plugins should return utf8-encoded bytes, which can be directly dumped to file.
Parameters: - fileformat (str) – the extension, uniquely specifying the file format.
- main_file_name (str) – (empty by default) Can be used by plugin to infer sensible names for additional files, if necessary. E.g. if the main file is ‘../myplot.gnu’, the plugin may decide to store the dat file under ‘../myplot_data.dat’.
- kwargs – other parameters are passed down to the plugin
Returns: a tuple of length 2. The first element is the content of the otuput file. The second is a dictionary (possibly empty) in the format {filename: filecontent} for any additional file that should be produced.
Return type: (bytes, dict)
-
_get_converters()[source]¶ Get all implemented converter formats. The convention is to find all _get_object_… methods. Returns a list of strings.
-
_get_exporters()[source]¶ Get all implemented export formats. The convention is to find all _prepare_… methods. Returns a dictionary of method_name: method_function
-
_get_importers()[source]¶ Get all implemented import formats. The convention is to find all _parse_… methods. Returns a list of strings.
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.data.Data.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.data.'¶
-
_source_attributes= ['db_name', 'db_uri', 'uri', 'id', 'version', 'extras', 'source_md5', 'description', 'license']¶
-
_storable= True¶
-
_unstorable_message= 'storing for this node has been disabled'¶
-
_validate()[source]¶ Perform validation of the Data object.
Note
validation of data source checks license and requires attribution to be provided in field ‘description’ of source in the case of any CC-BY* license. If such requirement is too strict, one can remove/comment it out.
-
convert(object_format=None, *args)[source]¶ Convert the AiiDA StructureData into another python object
Parameters: object_format – Specify the output format
-
creator¶ Return the creator of this node or None if it does not exist.
Returns: the creating node or None
-
export(path, fileformat=None, overwrite=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Save a Data object to a file.
Parameters: - fname – string with file name. Can be an absolute or relative path.
- fileformat – kind of format to use for the export. If not present, it will try to use the extension of the file name.
- overwrite – if set to True, overwrites file found at path. Default=False
- kwargs – additional parameters to be passed to the _exportcontent method
Returns: the list of files created
-
classmethod
get_export_formats()[source]¶ Get the list of valid export format strings
Returns: a list of valid formats
-
importfile(fname, fileformat=None)[source]¶ Populate a Data object from a file.
Parameters: - fname – string with file name. Can be an absolute or relative path.
- fileformat – kind of format to use for the export. If not present, it will try to use the extension of the file name.
-
importstring(inputstring, fileformat, **kwargs)[source]¶ Converts a Data object to other text format.
Parameters: fileformat – a string (the extension) to describe the file format. Returns: a string with the structure description.
-
source¶ Gets the dictionary describing the source of Data object. Possible fields:
- db_name: name of the source database.
- db_uri: URI of the source database.
- uri: URI of the object’s source. Should be a permanent link.
- id: object’s source identifier in the source database.
- version: version of the object’s source.
- extras: a dictionary with other fields for source description.
- source_md5: MD5 checksum of object’s source.
- description: human-readable free form description of the object’s source.
- license: a string with a type of license.
Note
some limitations for setting the data source exist, see
_validatemethod.Returns: dictionary describing the source of Data object.
-
Data sub class to represent a dictionary.
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.dict.Dict(**kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.DataData sub class to represent a dictionary.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(**kwargs)[source]¶ Store a dictionary as a Node instance.
Usual rules for attribute names apply, in particular, keys cannot start with an underscore, or a ValueError will be raised.
Initial attributes can be changed, deleted or added as long as the node is not stored.
Parameters: dict – the dictionary to set
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.dict'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.dict.Dict.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.dict.'¶
-
dict¶ Return an instance of AttributeManager that transforms the dictionary into an attribute dict.
Note
this will allow one to do node.dict.key as well as node.dict[key].
Returns: an instance of the AttributeResultManager.
-
keys()[source]¶ Iterator of valid keys stored in the Dict object.
Returns: iterator over the keys of the current dictionary
-
Data sub class to represent a float value.
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.float.Float(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.numeric.NumericTypeData sub class to represent a float value.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.float'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.float.Float.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.float.'¶
-
_type¶ alias of
__builtin__.float
-
Data sub class to represent a folder on a file system.
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.folder.FolderData(backend=None, user=None, computer=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.DataData sub class to represent a folder on a file system.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.folder'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.folder.FolderData.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.folder.'¶
-
Data sub class to represent an integer value.
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.int.Int(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.numeric.NumericTypeData sub class to represent an integer value.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.int'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.int.Int.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.int.'¶
-
_type¶ alias of
__builtin__.int
-
Data sub class to represent a list.
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.list.List(**kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.Data,_abcoll.MutableSequenceData sub class to represent a list.
-
_LIST_KEY= 'list'¶
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(**kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.list'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 102¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.list.List.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.list.'¶
-
_using_list_reference()[source]¶ This function tells the class if we are using a list reference. This means that calls to self.get_list return a reference rather than a copy of the underlying list and therefore self.set_list need not be called. This knwoledge is essential to make sure this class is performant.
Currently the implementation assumes that if the node needs to be stored then it is using the attributes cache which is a reference.
Returns: True if using self.get_list returns a reference to the underlying sequence. False otherwise. Return type: bool
-
index(value) → integer -- return first index of value.[source]¶ Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
-
pop([index]) → item -- remove and return item at index (default last).[source]¶ Raise IndexError if list is empty or index is out of range.
-
Module for defintion of base Data sub class for numeric based data types.
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.numeric.NumericType(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.base.BaseTypeSub class of Data to store numbers, overloading common operators (
+,*, …).-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.numeric'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.numeric.NumericType.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.numeric.'¶
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.orbital.OrbitalData(backend=None, user=None, computer=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.DataUsed for storing collections of orbitals, as well as providing methods for accessing them internally.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.orbital'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_get_orbital_class_from_orbital_dict(orbital_dict)[source]¶ Gets the orbital class from the orbital dictionary stored in DB
Parameters: orbital_dict – orbital dictionary associated with the orbital Returns: an Orbital produced using the module_name
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.orbital.OrbitalData.'¶
-
static
_prep_orbital_dict_keys_from_site(site)[source]¶ Prepares the position from an input site.
Parameters: site – a site of site class Return out_dict: a dictionary of attributes parsed from the site (currently only position)
-
_query_type_string= 'data.orbital.'¶
-
clear_orbitals()[source]¶ Remove all orbitals that were added to the class Cannot work if OrbitalData has been already stored
-
get_orbitals(with_tags=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Returns all orbitals by default. If a site is provided, returns all orbitals cooresponding to the location of that site, additional arguments may be provided, which act as filters on the retrieved orbitals.
Parameters: - site – if provided, returns all orbitals with position of site
- with_tags – if provided returns all tags stored
Kwargs: attributes than can filter the set of returned orbitals
Return list_of_outputs: a list of orbitals and also tags if with_tags was set to True
-
set_orbitals(orbital, tag=None)[source]¶ Sets the orbitals into the database. Uses the orbital’s inherent set_orbital_dict method to generate a orbital dict string at is stored along with the tags, if provided.
Parameters: - orbital – an orbital or list of orbitals to be set
- tag – a list of strings must be of length orbital
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.remote.RemoteData(remote_path=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.DataStore a link to a file or folder on a remote machine.
Remember to pass a computer!
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(remote_path=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.remote'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.remote.RemoteData.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.remote.'¶
-
_validate()[source]¶ Perform validation of the Data object.
Note
validation of data source checks license and requires attribution to be provided in field ‘description’ of source in the case of any CC-BY* license. If such requirement is too strict, one can remove/comment it out.
-
getfile(relpath, destpath)[source]¶ Connects to the remote folder and gets a string with the (full) content of the file.
Parameters: - relpath – The relative path of the file to show.
- destpath – A path on the local computer to get the file
Returns: a string with the file content
-
is_empty¶ Check if remote folder is empty
-
listdir(relpath='.')[source]¶ Connects to the remote folder and lists the directory content.
Parameters: relpath – If ‘relpath’ is specified, lists the content of the given subfolder. Returns: a flat list of file/directory names (as strings).
-
listdir_withattributes(path='.')[source]¶ Connects to the remote folder and lists the directory content.
Parameters: relpath – If ‘relpath’ is specified, lists the content of the given subfolder. Returns: a list of dictionaries, where the documentation is in :py:class:Transport.listdir_withattributes.
-
Data class that can be used to store a single file in its repository.
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.singlefile.SinglefileData(filepath, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.DataData class that can be used to store a single file in its repository.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(filepath, **kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.singlefile'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.singlefile.SinglefileData.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.singlefile.'¶
-
_validate()[source]¶ Ensure that there is one object stored in the repository, whose key matches value set for filename attr.
-
filename¶ Return the name of the file stored.
Returns: the filename under which the file is stored in the repository
-
get_content()[source]¶ Return the content of the single file stored for this data node.
Returns: the string content of the file
-
open(key=None, mode='r')[source]¶ Return an open file handle to the content of this data node.
Parameters: - key – optional key within the repository, by default is the filename set in the attributes
- mode – the mode with which to open the file handle
Returns: a file handle in read mode
-
Data sub class to represent a string value.
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.str.Str(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.base.BaseTypeData sub class to represent a string value.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.str'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.str.Str.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.str.'¶
-
_type¶ alias of
__builtin__.str
-
This module defines the classes for structures and all related functions to operate on them.
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure.StructureData(cell=None, pbc=None, ase=None, pymatgen=None, pymatgen_structure=None, pymatgen_molecule=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.data.DataThis class contains the information about a given structure, i.e. a collection of sites together with a cell, the boundary conditions (whether they are periodic or not) and other related useful information.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(cell=None, pbc=None, ase=None, pymatgen=None, pymatgen_structure=None, pymatgen_molecule=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_adjust_default_cell(vacuum_factor=1.0, vacuum_addition=10.0, pbc=(False, False, False))[source]¶ If the structure was imported from an xyz file, it lacks a defined cell, and the default cell is taken ([[1,0,0], [0,1,0], [0,0,1]]), leading to an unphysical definition of the structure. This method will adjust the cell
-
_dimensionality_label= {0: '', 1: 'length', 2: 'surface', 3: 'volume'}¶
-
_get_cif(converter='ase', store=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Creates
aiida.orm.nodes.data.cif.CifData.Parameters: - converter – specify the converter. Default ‘ase’.
- store – If True, intermediate calculation gets stored in the AiiDA database for record. Default False.
Returns:
-
_get_object_ase()[source]¶ Converts
StructureDatato ase.AtomsReturns: an ase.Atoms object
-
_get_object_phonopyatoms()[source]¶ Converts StructureData to PhonopyAtoms
Returns: a PhonopyAtoms object
-
_get_object_pymatgen(**kwargs)[source]¶ Converts
StructureDatato pymatgen objectReturns: a pymatgen Structure for structures with periodic boundary conditions (in three dimensions) and Molecule otherwise Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.0.13, usage of earlier versions may cause errors).
-
_get_object_pymatgen_molecule(**kwargs)[source]¶ Converts
StructureDatato pymatgen Molecule objectReturns: a pymatgen Molecule object corresponding to this StructureDataobject.Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.0.13, usage of earlier versions may cause errors)
-
_get_object_pymatgen_structure(**kwargs)[source]¶ Converts
StructureDatato pymatgen Structure object :param add_spin: True to add the spins to the pymatgen structure. Default is False (no spin added).Note
The spins are set according to the following rule:
- if the kind name ends with 1 -> spin=+1
- if the kind name ends with 2 -> spin=-1
Returns: a pymatgen Structure object corresponding to this StructureDataobjectRaises: ValueError – if periodic boundary conditions does not hold in at least one dimension of real space; if there are partial occupancies together with spins (defined by kind names ending with ‘1’ or ‘2’). Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.0.13, usage of earlier versions may cause errors)
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.structure.StructureData.'¶
-
_prepare_chemdoodle(main_file_name='')[source]¶ Write the given structure to a string of format required by ChemDoodle.
-
_prepare_tcod(main_file_name='', **kwargs)[source]¶ Write the given structure to a string of format TCOD CIF.
-
_prepare_xsf(main_file_name='')[source]¶ Write the given structure to a string of format XSF (for XCrySDen).
-
_query_type_string= 'data.structure.'¶
-
_set_incompatibilities= [('ase', 'cell'), ('ase', 'pbc'), ('ase', 'pymatgen'), ('ase', 'pymatgen_molecule'), ('ase', 'pymatgen_structure'), ('cell', 'pymatgen'), ('cell', 'pymatgen_molecule'), ('cell', 'pymatgen_structure'), ('pbc', 'pymatgen'), ('pbc', 'pymatgen_molecule'), ('pbc', 'pymatgen_structure'), ('pymatgen', 'pymatgen_molecule'), ('pymatgen', 'pymatgen_structure'), ('pymatgen_molecule', 'pymatgen_structure')]¶
-
append_atom(**kwargs)[source]¶ Append an atom to the Structure, taking care of creating the corresponding kind.
Parameters: - ase – the ase Atom object from which we want to create a new atom (if present, this must be the only parameter)
- position – the position of the atom (three numbers in angstrom)
- symbols – passed to the constructor of the Kind object.
- weights – passed to the constructor of the Kind object.
- name – passed to the constructor of the Kind object. See also the note below.
Note
Note on the ‘name’ parameter (that is, the name of the kind):
- if specified, no checks are done on existing species. Simply, a new kind with that name is created. If there is a name clash, a check is done: if the kinds are identical, no error is issued; otherwise, an error is issued because you are trying to store two different kinds with the same name.
- if not specified, the name is automatically generated. Before adding the kind, a check is done. If other species with the same properties already exist, no new kinds are created, but the site is added to the existing (identical) kind. (Actually, the first kind that is encountered). Otherwise, the name is made unique first, by adding to the string containing the list of chemical symbols a number starting from 1, until an unique name is found
Note
checks of equality of species are done using the
compare_with()method.
-
append_kind(kind)[source]¶ Append a kind to the
StructureData. It makes a copy of the kind.Parameters: kind – the site to append, must be a Kind object.
-
append_site(site)[source]¶ Append a site to the
StructureData. It makes a copy of the site.Parameters: site – the site to append. It must be a Site object.
-
cell¶ Returns the cell shape.
Returns: a 3x3 list of lists.
-
cell_angles¶ Get the angles between the cell lattice vectors in degrees.
-
cell_lengths¶ Get the lengths of cell lattice vectors in angstroms.
-
get_ase()[source]¶ Get the ASE object. Requires to be able to import ase.
Returns: an ASE object corresponding to this StructureDataobject.Note
If any site is an alloy or has vacancies, a ValueError is raised (from the site.get_ase() routine).
-
get_cif(converter='ase', store=False, **kwargs)[source]¶ Creates
aiida.orm.nodes.data.cif.CifData.New in version 1.0: Renamed from _get_cif
Parameters: - converter – specify the converter. Default ‘ase’.
- store – If True, intermediate calculation gets stored in the AiiDA database for record. Default False.
Returns:
-
get_composition()[source]¶ Returns the chemical composition of this structure as a dictionary, where each key is the kind symbol (e.g. H, Li, Ba), and each value is the number of occurences of that element in this structure. For BaZrO3 it would return {‘Ba’:1, ‘Zr’:1, ‘O’:3}. No reduction with smallest common divisor!
Returns: a dictionary with the composition
-
get_description()[source]¶ Returns a string with infos retrieved from StructureData node’s properties
Parameters: self – the StructureData node Returns: retsrt: the description string
-
get_dimensionality()[source]¶ This function checks the dimensionality of the structure and calculates its length/surface/volume :return: returns the dimensionality and length/surface/volume
-
get_formula(mode='hill', separator='')[source]¶ Return a string with the chemical formula.
Parameters: - mode –
a string to specify how to generate the formula, can assume one of the following values:
- ’hill’ (default): count the number of atoms of each species,
then use Hill notation, i.e. alphabetical order with C and H
first if one or several C atom(s) is (are) present, e.g.
['C','H','H','H','O','C','H','H','H']will return'C2H6O'['S','O','O','H','O','H','O']will return'H2O4S'From E. A. Hill, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 22 (8), pp 478–494 (1900) - ’hill_compact’: same as hill but the number of atoms for each
species is divided by the greatest common divisor of all of them, e.g.
['C','H','H','H','O','C','H','H','H','O','O','O']will return'CH3O2' - ’reduce’: group repeated symbols e.g.
['Ba', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O', 'Ba', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O', 'Ba', 'Ti', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O']will return'BaTiO3BaTiO3BaTi2O3' - ’group’: will try to group as much as possible parts of the formula
e.g.
['Ba', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O', 'Ba', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O', 'Ba', 'Ti', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O']will return'(BaTiO3)2BaTi2O3' - ’count’: same as hill (i.e. one just counts the number
of atoms of each species) without the re-ordering (take the
order of the atomic sites), e.g.
['Ba', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O','Ba', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O']will return'Ba2Ti2O6' - ’count_compact’: same as count but the number of atoms
for each species is divided by the greatest common divisor of
all of them, e.g.
['Ba', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O','Ba', 'Ti', 'O', 'O', 'O']will return'BaTiO3'
- ’hill’ (default): count the number of atoms of each species,
then use Hill notation, i.e. alphabetical order with C and H
first if one or several C atom(s) is (are) present, e.g.
- separator – a string used to concatenate symbols. Default empty.
Returns: a string with the formula
Note
in modes reduce, group, count and count_compact, the initial order in which the atoms were appended by the user is used to group and/or order the symbols in the formula
- mode –
-
get_kind(kind_name)[source]¶ Return the kind object associated with the given kind name.
Parameters: kind_name – String, the name of the kind you want to get Returns: The Kind object associated with the given kind_name, if a Kind with the given name is present in the structure. Raise: ValueError if the kind_name is not present.
-
get_kind_names()[source]¶ Return a list of kind names (in the same order of the
self.kindsproperty, but return the names rather than Kind objects)Note
This is NOT necessarily a list of chemical symbols! Use get_symbols_set for chemical symbols
Returns: a list of strings.
-
get_pymatgen(**kwargs)[source]¶ Get pymatgen object. Returns Structure for structures with periodic boundary conditions (in three dimensions) and Molecule otherwise. :param add_spin: True to add the spins to the pymatgen structure. Default is False (no spin added).
Note
The spins are set according to the following rule:
- if the kind name ends with 1 -> spin=+1
- if the kind name ends with 2 -> spin=-1
Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.0.13, usage of earlier versions may cause errors).
-
get_pymatgen_molecule()[source]¶ Get the pymatgen Molecule object.
Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.0.13, usage of earlier versions may cause errors).
Returns: a pymatgen Molecule object corresponding to this StructureDataobject.
-
get_pymatgen_structure(**kwargs)[source]¶ Get the pymatgen Structure object. :param add_spin: True to add the spins to the pymatgen structure. Default is False (no spin added).
Note
The spins are set according to the following rule:
- if the kind name ends with 1 -> spin=+1
- if the kind name ends with 2 -> spin=-1
Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.0.13, usage of earlier versions may cause errors).
Returns: a pymatgen Structure object corresponding to this StructureDataobject.Raises: ValueError – if periodic boundary conditions do not hold in at least one dimension of real space.
-
get_site_kindnames()[source]¶ Return a list with length equal to the number of sites of this structure, where each element of the list is the kind name of the corresponding site.
Note
This is NOT necessarily a list of chemical symbols! Use
[ self.get_kind(s.kind_name).get_symbols_string() for s in self.sites]for chemical symbolsReturns: a list of strings
-
get_symbols_set()[source]¶ Return a set containing the names of all elements involved in this structure (i.e., for it joins the list of symbols for each kind k in the structure).
Returns: a set of strings of element names.
-
has_vacancies¶ Return whether the structure has vacancies in the structure.
Returns: a boolean, True if at least one kind has a vacancy
-
is_alloy¶ Return whether the structure contains any alloy kinds.
Returns: a boolean, True if at least one kind is an alloy
-
kinds¶ Returns a list of kinds.
-
pbc¶ Get the periodic boundary conditions.
Returns: a tuple of three booleans, each one tells if there are periodic boundary conditions for the i-th real-space direction (i=1,2,3)
-
reset_cell(new_cell)[source]¶ Reset the cell of a structure not yet stored to a new value.
Parameters: new_cell – list specifying the cell vectors Raises: ModificationNotAllowed: if object is already stored
-
reset_sites_positions(new_positions, conserve_particle=True)[source]¶ Replace all the Site positions attached to the Structure
Parameters: - new_positions – list of (3D) positions for every sites.
- conserve_particle – if True, allows the possibility of removing a site. currently not implemented.
Raises: - aiida.common.ModificationNotAllowed – if object is stored already
- ValueError – if positions are invalid
Note
it is assumed that the order of the new_positions is given in the same order of the one it’s substituting, i.e. the kind of the site will not be checked.
-
set_pymatgen(obj, **kwargs)[source]¶ Load the structure from a pymatgen object.
Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.0.13, usage of earlier versions may cause errors).
-
set_pymatgen_molecule(mol, margin=5)[source]¶ Load the structure from a pymatgen Molecule object.
Parameters: margin – the margin to be added in all directions of the bounding box of the molecule. Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.0.13, usage of earlier versions may cause errors).
-
set_pymatgen_structure(struct)[source]¶ Load the structure from a pymatgen Structure object.
Note
periodic boundary conditions are set to True in all three directions.
Note
Requires the pymatgen module (version >= 3.3.5, usage of earlier versions may cause errors).
Raises: ValueError – if there are partial occupancies together with spins.
-
sites¶ Returns a list of sites.
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure.Kind(**kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
objectThis class contains the information about the species (kinds) of the system.
It can be a single atom, or an alloy, or even contain vacancies.
-
__dict__= dict_proxy({'__module__': 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure', 'symbol': <property object>, 'symbols': <property object>, '__dict__': <attribute '__dict__' of 'Kind' objects>, 'get_symbols_string': <function get_symbols_string>, '__init__': <function __init__>, 'is_alloy': <property object>, 'compare_with': <function compare_with>, 'name': <property object>, 'has_vacancies': <property object>, '__weakref__': <attribute '__weakref__' of 'Kind' objects>, 'reset_mass': <function reset_mass>, 'set_automatic_kind_name': <function set_automatic_kind_name>, '__doc__': '\n This class contains the information about the species (kinds) of the system.\n\n It can be a single atom, or an alloy, or even contain vacancies.\n ', 'get_raw': <function get_raw>, 'set_symbols_and_weights': <function set_symbols_and_weights>, 'mass': <property object>, '__repr__': <function __repr__>, 'weights': <property object>, '__str__': <function __str__>})¶
-
__init__(**kwargs)[source]¶ Create a site. One can either pass:
Parameters: - raw – the raw python dictionary that will be converted to a Kind object.
- ase – an ase Atom object
- kind – a Kind object (to get a copy)
Or alternatively the following parameters:
Parameters: - symbols – a single string for the symbol of this site, or a list of symbol strings
- weights – (optional) the weights for each atomic species of this site. If only a single symbol is provided, then this value is optional and the weight is set to 1.
- mass – (optional) the mass for this site in atomic mass units. If not provided, the mass is set by the self.reset_mass() function.
- name – a string that uniquely identifies the kind, and that is used to identify the sites.
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure'¶
-
__weakref__¶ list of weak references to the object (if defined)
-
compare_with(other_kind)[source]¶ Compare with another Kind object to check if they are different.
Note
This does NOT check the ‘type’ attribute. Instead, it compares (with reasonable thresholds, where applicable): the mass, and the list of symbols and of weights. Moreover, it compares the
_internal_tag, if defined (at the moment, defined automatically only when importing the Kind from ASE, if the atom has a non-zero tag). Note that the _internal_tag is only used while the class is loaded, but is not persisted on the database.Returns: A tuple with two elements. The first one is True if the two sites are ‘equivalent’ (same mass, symbols and weights), False otherwise. The second element of the tuple is a string, which is either None (if the first element was True), or contains a ‘human-readable’ description of the first difference encountered between the two sites.
-
get_raw()[source]¶ Return the raw version of the site, mapped to a suitable dictionary. This is the format that is actually used to store each kind of the structure in the DB.
Returns: a python dictionary with the kind.
-
get_symbols_string()[source]¶ Return a string that tries to match as good as possible the symbols of this kind. If there is only one symbol (no alloy) with 100% occupancy, just returns the symbol name. Otherwise, groups the full string in curly brackets, and try to write also the composition (with 2 precision only).
Note
If there is a vacancy (sum of weights<1), we indicate it with the X symbol followed by 1-sum(weights) (still with 2 digits precision, so it can be 0.00)
Note
Note the difference with respect to the symbols and the symbol properties!
-
has_vacancies¶ Return whether the Kind contains vacancies, i.e. when the sum of the weights is less than one.
Note
the property uses the internal variable _sum_threshold as a threshold.
Returns: boolean, True if the sum of the weights is less than one, False otherwise
-
is_alloy¶ Return whether the Kind is an alloy, i.e. contains more than one element
Returns: boolean, True if the kind has more than one element, False otherwise.
-
mass¶ The mass of this species kind.
Returns: a float
-
name¶ Return the name of this kind. The name of a kind is used to identify the species of a site.
Returns: a string
-
reset_mass()[source]¶ Reset the mass to the automatic calculated value.
The mass can be set manually; by default, if not provided, it is the mass of the constituent atoms, weighted with their weight (after the weight has been normalized to one to take correctly into account vacancies).
This function uses the internal _symbols and _weights values and thus assumes that the values are validated.
It sets the mass to None if the sum of weights is zero.
-
set_automatic_kind_name(tag=None)[source]¶ Set the type to a string obtained with the symbols appended one after the other, without spaces, in alphabetical order; if the site has a vacancy, a X is appended at the end too.
-
set_symbols_and_weights(symbols, weights)[source]¶ Set the chemical symbols and the weights for the site.
Note
Note that the kind name remains unchanged.
-
symbol¶ If the kind has only one symbol, return it; otherwise, raise a ValueError.
-
symbols¶ List of symbols for this site. If the site is a single atom, pass a list of one element only, or simply the string for that atom. For alloys, a list of elements.
Note
Note that if you change the list of symbols, the kind name remains unchanged.
-
weights¶ Weights for this species kind. Refer also to :func:validate_symbols_tuple for the validation rules on the weights.
-
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure.Site(**kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
objectThis class contains the information about a given site of the system.
It can be a single atom, or an alloy, or even contain vacancies.
-
__dict__= dict_proxy({'__module__': 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure', 'kind_name': <property object>, '__str__': <function __str__>, 'get_raw': <function get_raw>, 'get_ase': <function get_ase>, '__repr__': <function __repr__>, '__dict__': <attribute '__dict__' of 'Site' objects>, 'position': <property object>, '__weakref__': <attribute '__weakref__' of 'Site' objects>, '__doc__': '\n This class contains the information about a given site of the system.\n\n It can be a single atom, or an alloy, or even contain vacancies.\n ', '__init__': <function __init__>})¶
-
__init__(**kwargs)[source]¶ Create a site.
Parameters: - kind_name – a string that identifies the kind (species) of this site. This has to be found in the list of kinds of the StructureData object. Validation will be done at the StructureData level.
- position – the absolute position (three floats) in angstrom
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.structure'¶
-
__weakref__¶ list of weak references to the object (if defined)
-
get_ase(kinds)[source]¶ Return a ase.Atom object for this site.
Parameters: kinds – the list of kinds from the StructureData object. Note
If any site is an alloy or has vacancies, a ValueError is raised (from the site.get_ase() routine).
-
get_raw()[source]¶ Return the raw version of the site, mapped to a suitable dictionary. This is the format that is actually used to store each site of the structure in the DB.
Returns: a python dictionary with the site.
-
kind_name¶ Return the kind name of this site (a string).
The type of a site is used to decide whether two sites are identical (same mass, symbols, weights, …) or not.
-
position¶ Return the position of this site in absolute coordinates, in angstrom.
-
This module manages the UPF pseudopotentials in the local repository.
-
class
aiida.orm.nodes.data.upf.UpfData(filepath=None, source=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Bases:
aiida.orm.nodes.data.singlefile.SinglefileDataFunction not yet documented.
-
__abstractmethods__= frozenset([])¶
-
__init__(filepath=None, source=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Parameters: backend_entity ( aiida.orm.implementation.BackendEntity) – the backend model supporting this entity
-
__module__= 'aiida.orm.nodes.data.upf'¶
-
_abc_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_abc_negative_cache_version= 40¶
-
_abc_registry= <_weakrefset.WeakSet object>¶
-
_logger= <logging.Logger object>¶
-
_plugin_type_string= 'data.upf.UpfData.'¶
-
_query_type_string= 'data.upf.'¶
-
_validate()[source]¶ Ensure that there is one object stored in the repository, whose key matches value set for filename attr.
-
element¶
-
classmethod
from_md5(md5)[source]¶ Return a list of all UPF pseudopotentials that match a given MD5 hash.
Note that the hash has to be stored in a _md5 attribute, otherwise the pseudo will not be found.
-
classmethod
get_or_create(filepath, use_first=False, store_upf=True)[source]¶ Pass the same parameter of the init; if a file with the same md5 is found, that UpfData is returned.
Parameters: - filepath – an absolute filepath on disk
- use_first – if False (default), raise an exception if more than one potential is found. If it is True, instead, use the first available pseudopotential.
- store_upf (bool) – If false, the UpfData objects are not stored in the database. default=True.
Return (upf, created): where upf is the UpfData object, and create is either True if the object was created, or False if the object was retrieved from the DB.
-
classmethod
get_upf_groups(filter_elements=None, user=None)[source]¶ Return all names of groups of type UpfFamily, possibly with some filters.
Parameters: - filter_elements – A string or a list of strings. If present, returns only the groups that contains one Upf for every element present in the list. Default=None, meaning that all families are returned.
- user – if None (default), return the groups for all users. If defined, it should be either a DbUser instance, or a string for the username (that is, the user email).
-
md5sum¶
-
store(*args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Store the node, reparsing the file so that the md5 and the element are correctly reset.
-
upffamily_type_string= 'data.upf'¶
-